Overview
Kafka MirrorMaker 2 (MM2) represents a significant evolution in Kafka's cross-cluster replication capabilities. Introduced in Kafka 2.4.0 through KIP-382, MM2 addresses the limitations of its predecessor by leveraging the Kafka Connect framework to provide a robust, scalable solution for data replication across Kafka clusters. This comprehensive guide explores MM2's architecture, configuration, and best practices for optimal implementation.
Core Architecture and Components
MirrorMaker 2 is built on the Kafka Connect framework, which provides a distributed, fault-tolerant foundation for data replication. Unlike the original MirrorMaker that used a simple consumer-producer pair, MM2 employs specialized connectors to handle different aspects of the replication process.
![Mirror Maker 2 Connector [25]](/blog/kafka-mirrormaker-2-usages-best-practices/1.png)
The Four Essential Connectors
MM2's architecture consists of four primary connectors, each serving a distinct purpose in the replication workflow:
| Connector | Primary Responsibility | Details |
|---|---|---|
| MirrorSourceConnector | Replicates topic data and metadata | Replicates topics, ACLs, and configurations from source cluster; emits offset-syncs to internal topics |
| MirrorSinkConnector | Transfers data to target cluster | Consumes from primary cluster and replicates data to target cluster |
| MirrorCheckpointConnector | Manages consumer offset translation | Consumes offset-syncs and emits checkpoints for failover scenarios |
| MirrorHeartbeatConnector | Monitors replication health | Emits heartbeats to remote clusters for monitoring replication latency and availability |
These connectors work together to create a comprehensive replication system that not only transfers data but also maintains configuration consistency and enables consumer migration between clusters.
Key Features
Automated Topic Management
MM2 automatically detects new topics and partitions in the source cluster, eliminating the need for manual intervention when adding new topics. It also synchronizes topic configurations between clusters, ensuring consistent settings across environments.
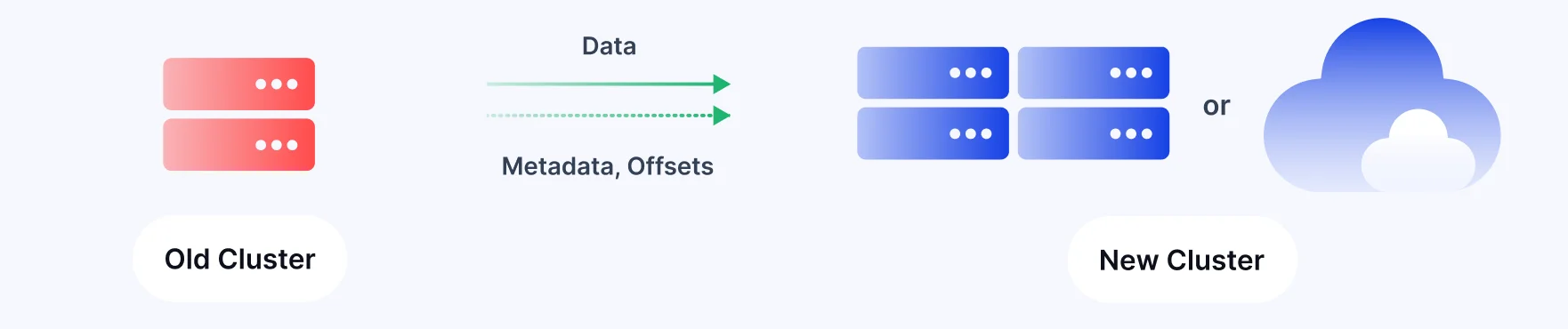
Consumer Group Offset Translation
One of MM2's most valuable features is its ability to translate consumer group offsets between clusters. This enables seamless consumer migration during failover scenarios, maintaining exactly-once semantics for consumer groups.
Flexible Replication Topologies
MM2 supports various replication topologies, including:
-
Active-passive for disaster recovery
-
Active-active for bidirectional replication
-
Hub-and-spoke for data aggregation
-
Multi-region for geographic distribution
Common Use Cases
Disaster Recovery
MM2 enables organizations to implement robust disaster recovery strategies by continuously replicating data to a backup cluster. In the event of a primary cluster failure, applications can seamlessly switch to the backup cluster with minimal disruption since MM2 maintains consumer offset mappings between clusters.
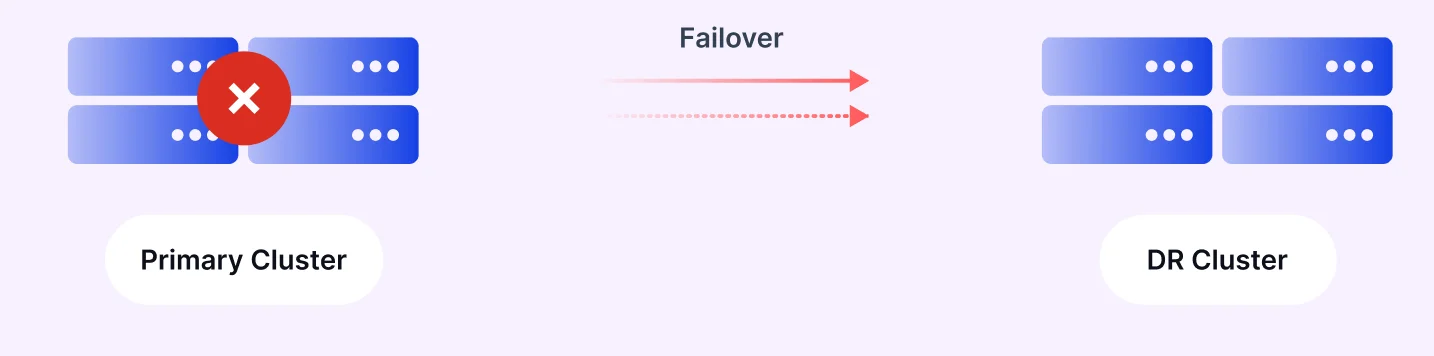
Geographic Replication
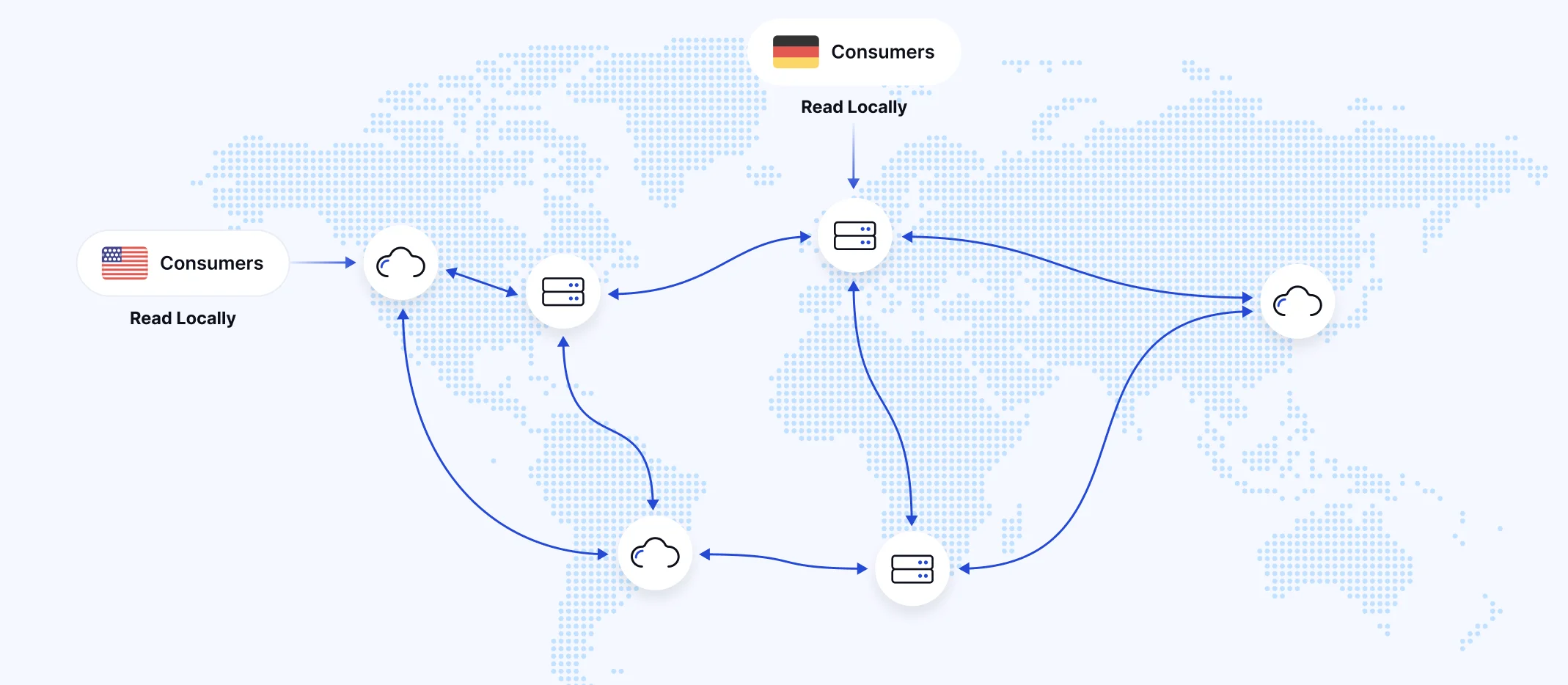
For organizations with global operations, MM2 facilitates replicating data across multiple regions, improving data locality and reducing access times for geographically distributed applications. This follows the "Best Practice: Consume from remote, produce to local" pattern as noted in the Instaclustr blog .
Data Isolation
MM2 allows organizations to create separate environments for different purposes such as testing, development, or compliance requirements. Each environment can have its own Kafka cluster with necessary data replicated from production.
Data Aggregation
For organizations with multiple Kafka clusters, MM2 can aggregate data into a central cluster for analytics, reporting, or other purposes, enabling centralized processing while maintaining decentralized production environments.
Comparison with Alternatives
Several alternatives to MM2 exist for cross-cluster replication:
| Solution | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| MirrorMaker 2 | Open source, Connect framework integration, offset translation | Performance tuning required for high throughput |
| Confluent Replicator | Control Center integration, commercial support | Proprietary, licensing costs |
| AutoMQ Kafka Linking | Supports data migration with checkpoint retention.Supports zero-downtime migration and automated traffic switching. | Primarily for migrating Kafka to AutoMQ service. |
| Cluster Linking | Native Kafka feature, simplified architecture | Newer feature with less community experience |
| Conduktor Gateway | Seamless cluster switching for failover | Does not handle replication itself |
DeploymentGuide
Basic Configuration Parameters
A typical MM2 configuration file includes the following essential parameters:
# Specify cluster aliases
clusters = source, destination
# Connection information
source.bootstrap.servers = source-kafka-1:9092,source-kafka-2:9092
destination.bootstrap.servers = dest-kafka-1:9092,dest-kafka-2:9092
# Enable replication flow
source->destination.enabled = true
# Topics to replicate (regex)
source->destination.topics = topic-pattern-.*
# Replication factor settings
replication.factor = 3
checkpoints.topic.replication.factor = 1
heartbeats.topic.replication.factor = 1
offset-syncs.topic.replication.factor = 1Deployment Methods
MM2 can be deployed using several methods:
- Using the
connect-mirror-maker.shscript included in the Kafka distribution:
./bin/connect-mirror-maker.sh ./config/mirror-maker.properties-
Using container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes with operators such as Strimzi that provide a
KafkaMirrorMaker2custom resource. -
Through managed services like Aiven or Instaclustr that offer MirrorMaker 2 as a managed service.
Performance Tuning for High Throughput
When dealing with high-throughput topics, default MM2 configurations often prove insufficient. Based on recommendations from Klarrio and other sources, the following parameters require careful tuning:
| Parameter | Description | Recommended Value for High Throughput |
|---|---|---|
| max.partition.fetch.bytes | Maximum bytes fetched per partition | 50MiB (52,428,800 bytes) |
| batch.size | Maximum producer batch size | 50MiB (matching fetch size) |
| linger.ms | Time to wait for batch to fill | 100ms or higher for WAN replication |
| fetch.min.bytes | Minimum data to fetch | 1MiB (1,048,576 bytes) |
| buffer.memory | Producer buffer memory | 500MiB (524,288,000 bytes) |
| num.stream.threads | Consumer threads | Test with 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 24, and 32 threads |
For replication across high-latency networks, larger batch sizes become essential. Research shows that with a 100ms round-trip time, small batches severely limit throughput. For optimal performance over WAN connections, batch sizes should be at least 32MiB.
Client Configuration Override in Kafka Connect
Because MM2 is built on Kafka Connect, configuring client settings requires special attention:
- First, enable configuration overrides in Connect's:
connector.client.config.override.policy=All-
Then use the correct prefixes for client configurations:
-
For source mode:
producer.override.*andsource.consumer.* -
For sink mode:
consumer.override.*andsink.producer.*
-
For example, to configure the consumer in source mode:
source.consumer.fetch.max.bytes=50000000
source.consumer.max.partition.fetch.bytes=50000000Known Issues and Limitations
Offset Translation Issues
MM2 may translate offsets incorrectly if LAG shows negative on the target cluster. According to Aiven's documentation , this issue is expected to be resolved in version 3.3.0.
Configuration Synchronization Limitations
MM2 doesn't fully replicate all topic configurations:
-
It always sets
min.insync.replicas = 1in destination topics, regardless of source configuration -
The replication factor of target topics may not match the source cluster's configuration
Topic Naming
By default, MM2 prefixes source cluster names to replicated topics (e.g., "source.topic-name"). While this helps prevent conflicts in complex replication topologies, it may not be desired in all cases.
Best Practices
Deployment Architecture
-
Deploy MM2 in the target data center to minimize latency for the critical consumer path
-
Run MM2 in a separate cluster from your Kafka brokers to isolate resource usage
-
Allocate sufficient resources based on the volume of data being replicated
Security Configuration
-
Implement proper security credentials for both source and target clusters
-
For the source cluster, configure read-only access to protect source data
-
For Kerberos-enabled clusters, properly configure JAAS
Monitoring and Management
-
Implement JMX monitoring for MM2 using tools like Prometheus and Grafana
-
Monitor key metrics including:
-
Replication latency
-
Consumer lag
-
Worker task states
-
Task errors
-
Topic Management
-
Use carefully designed topic patterns to include only necessary topics
-
Consider using blacklist patterns to exclude internal topics
-
For high-priority topics, consider dedicated MM2 instances with specific topic patterns
Failover Testing
-
Regularly test failover scenarios to ensure recovery procedures work as expected
-
Validate consumer offset translation during failover tests
-
Document and automate failover procedures for operational teams
Conclusion
Kafka MirrorMaker 2 significantly improved over its predecessor, offering robust functionality for cross-cluster data replication through the Kafka Connect framework. Its ability to maintain topic configurations, preserve consumer offsets, and support complex replication topologies makes it suitable for various use cases from disaster recovery to geo-replication.
While MM2 requires careful configuration and tuning for high-throughput scenarios, particularly over high-latency networks, it provides a flexible open-source solution for Kafka cluster replication. By following the best practices outlined in this guide and properly addressing known limitations, organizations can successfully implement MM2 for their Kafka replication needs.
Interested in our diskless Kafka solution AutoMQ? See how leading companies leverage AutoMQ in their production environments by reading our case studies. The source code is also available on GitHub.
-
Grab: Driving Efficiency with AutoMQ in DataStreaming Platform
-
Palmpay Uses AutoMQ to Replace Kafka, Optimizing Costs by 50%+
-
How Asia’s Quora Zhihu uses AutoMQ to reduce Kafka cost and maintenance complexity
-
XPENG Motors Reduces Costs by 50%+ by Replacing Kafka with AutoMQ
-
Asia's GOAT, Poizon uses AutoMQ Kafka to build observability platform for massive data(30 GB/s)
-
AutoMQ Helps CaoCao Mobility Address Kafka Scalability During Holidays
-
JD.com x AutoMQ x CubeFS: A Cost-Effective Journey at Trillion-Scale Kafka Messaging