Intro test test publish blog
If you're interested in messaging or streaming systems, you've definitely heard of Kafka. Chances are, you've also come across countless solutions claiming to be better than Kafka.
This proves two things: First, more and more companies are incorporating Kafka into their infrastructure thanks to its versatility (a growing market). Second, many users struggle with operating Kafka, especially in this cloud era (pain points to resolve).
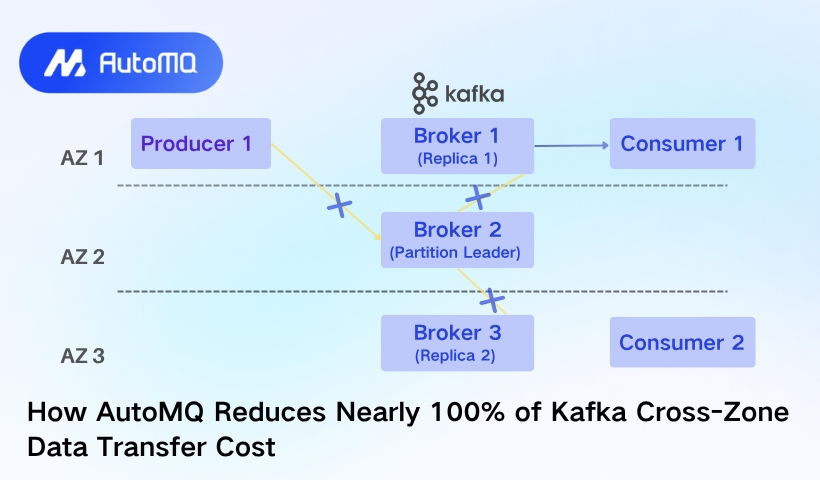
When bringing Apache Kafka to the cloud, its replication factor causes the leader to send received data to other followers in different Availability Zones (AZs). The data transfer cost may not seem obvious at first compared to compute and storage costs; however, based on observations from Confluent, cross-AZ transfer costs can surprisingly account for more than 50% of the total bill (more on this later).
In the WarpStream article that I published not long ago, we found that WarpStream avoids cross-AZ transfer costs by hacking the service discovery to ensure that the client always communicates with the broker in the same AZ. WarpStream’s rewriting of the Kafka protocol plays a vital role here.
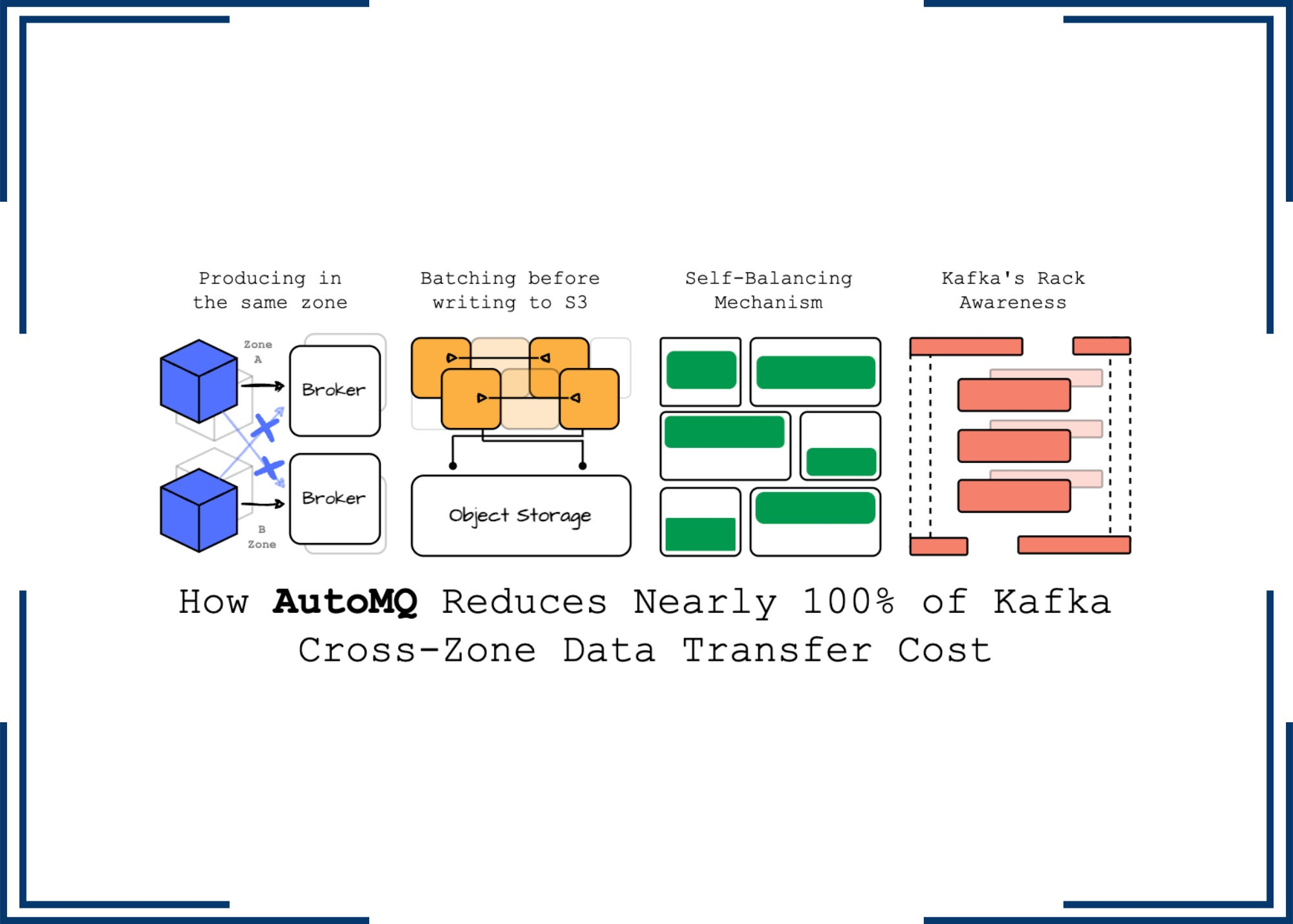
This week, we will explore how AutoMQ, a 100% Kafka-compatible alternative solution, can help users significantly reduce cross-AZ transfer costs. The solution is designed to run Kafka efficiently on the cloud by leveraging Kafka’s codebase for the protocol and rewriting the storage layer so it can effectively offload data to object storage with the introduction of the WAL.
I’ve written a detailed article about AutoMQ not long ago; you can find ithere.
Here’s the structure of this article: First, we’ll review Confluent’s observation on Apache Kafka. Then, we’ll provide an overview of AutoMQ, and finally, we’ll discover how AutoMQ can help users reduce data transfer costs.
For my convenience in delivering insights, AutoMQ features are described using AWS services such as S3 or EBS.









.png)