Kafka Access Control Lists (ACLs) provide a robust authorization framework that determines which authenticated users can perform specific operations on Kafka resources. This comprehensive guide explores Kafka ACL concepts, configuration approaches, management tools, and best practices for implementing effective authorization in your Kafka deployments.
Understanding Kafka Authorization and ACLs
Kafka authorization determines what an authenticated entity can do once its identity has been verified. Similar to how an ATM allows you access only to your accounts after PIN verification, Kafka enables specific actions for authenticated clients based on their permissions. Authorization in Kafka is implemented through Access Control Lists (ACLs), which specify which users can perform which operations on specific resources.
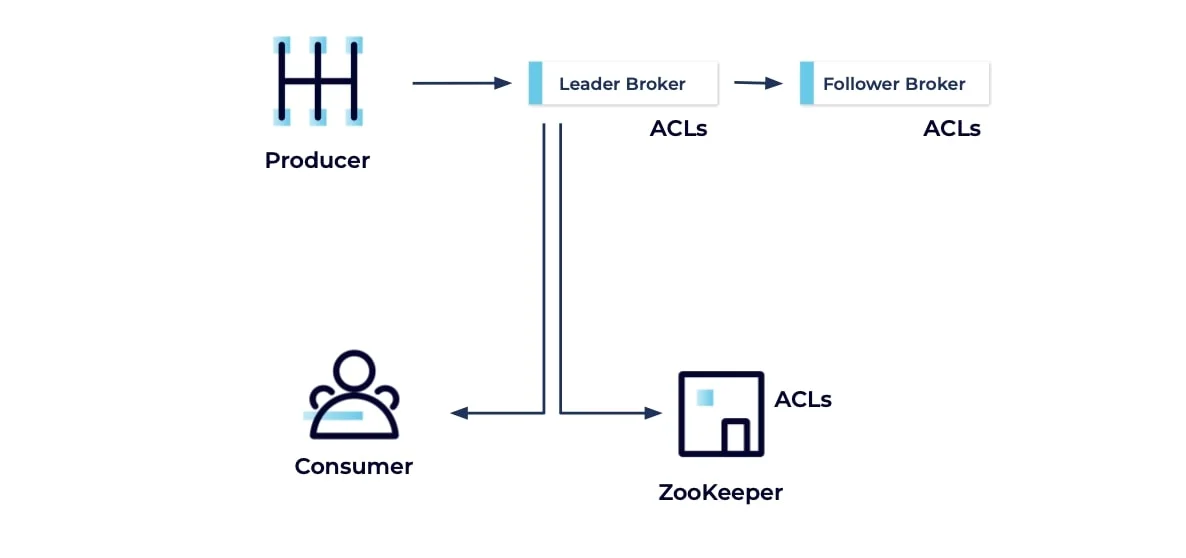
Core Authorization Concepts
The authorization framework in Kafka is pluggable and configured using the authorizer.class.name property. Two primary authorizer implementations are available:
-
AclAuthorizer : For ZooKeeper-based clusters, storing ACLs in ZooKeeper
-
StandardAuthorizer : For KRaft-based clusters, storing ACLs in the cluster metadata
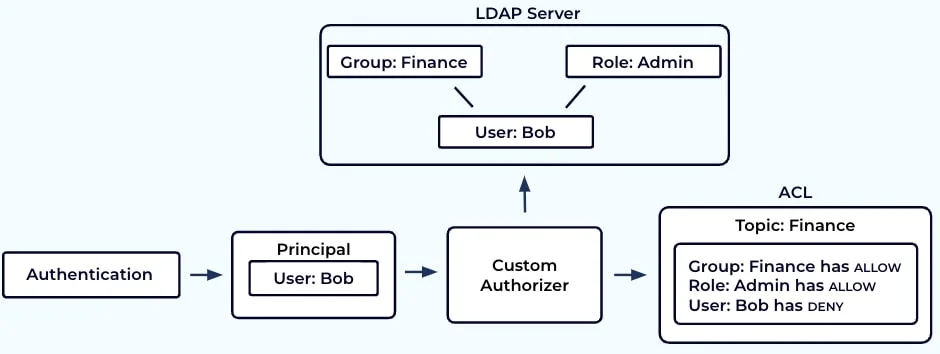
Each ACL consists of five core components that together define a permission:
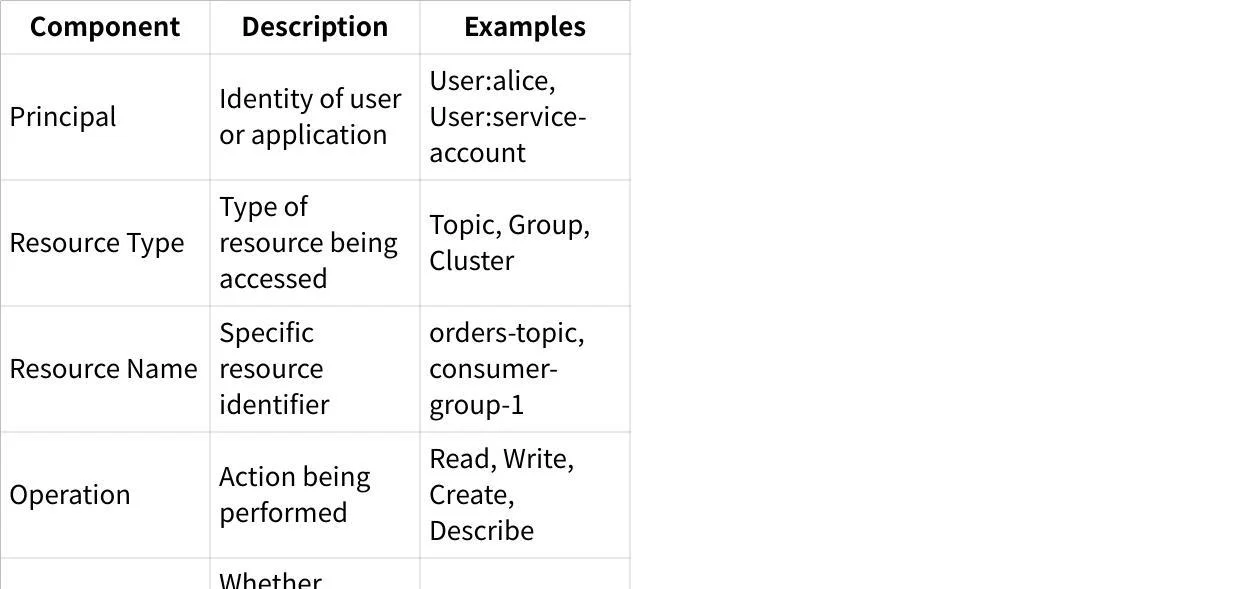
Additionally, ACLs can specify a host parameter (IP address) to limit connections from specific locations, and pattern types (LITERAL, PREFIX, or WILDCARD) to match resources.
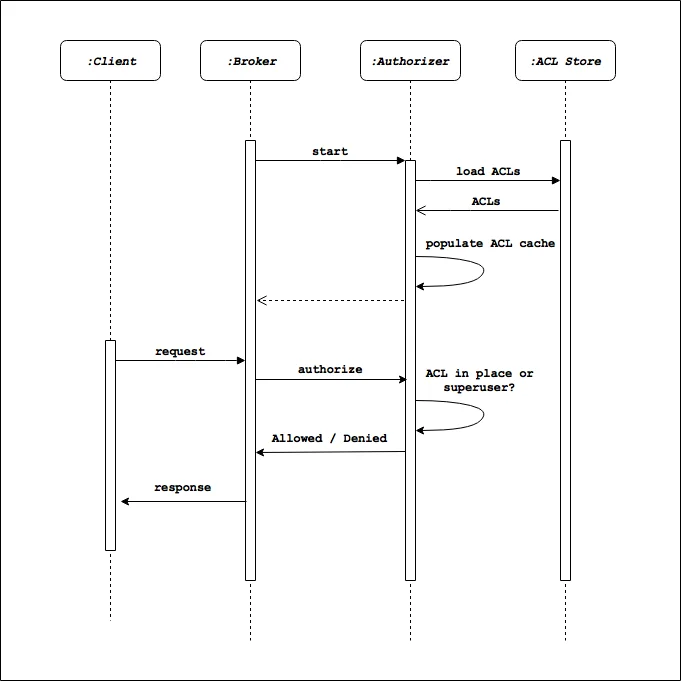
The Default Behavior
By default, if a resource has no associated ACLs, access is determined by the allow.everyone.if.no.acl.found property. Amazon MSK sets this to true by default, meaning resources without explicit ACLs are accessible to all principals. However, once you add ACLs to a resource, only authorized principals can access it.
SASL Authentication with Kafka ACLs
Before authorization can occur, clients must be authenticated. Kafka commonly uses Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL) mechanisms, which provide the authenticated identities that ACLs reference.
SASL Mechanisms for Authentication
Kafka supports several SASL mechanisms, each with different security characteristics:
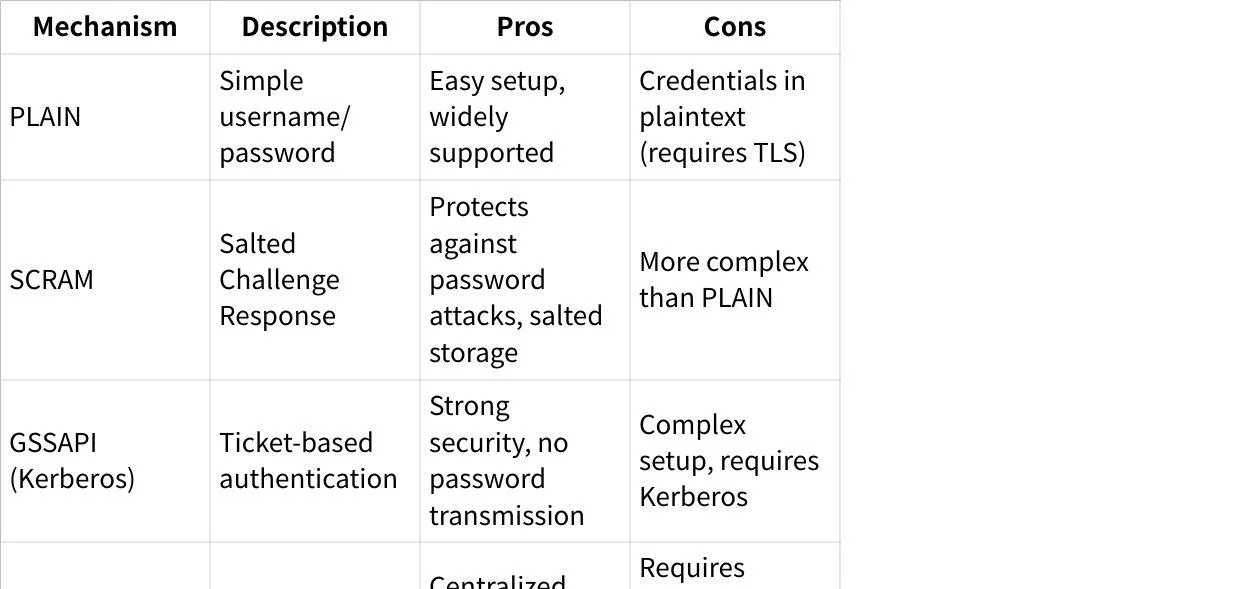
It's important to distinguish between SASL/PLAIN (the authentication mechanism) and SASL_PLAINTEXT/SASL_SSL (the security protocol). The former refers to username/password credentials, while the latter indicates whether the connection is encrypted with TLS.
Configuring Kafka ACLs
Setting up ACLs involves both broker and client configuration steps.
Broker Configuration
To enable ACL authorization on Kafka brokers, add the following to server.properties :
# Enable ACL authorization
authorizer.class.name=kafka.security.authorizer.AclAuthorizer
# Default permission when no ACLs exist for a resource
allow.everyone.if.no.acl.found=true
# Enable SASL mechanisms
sasl.enabled.mechanisms=PLAIN,SCRAM-SHA-512
# Configure security protocol
listeners=SASL_SSL://hostname:9093
security.inter.broker.protocol=SASL_SSLJAAS Configuration
Java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS) configuration is essential for SASL authentication. For brokers, JAAS configuration should be prefixed with the listener name and SASL mechanism:
listener.name.sasl_ssl.plain.sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required \
username="admin" \
password="admin-secret" \
user_admin="admin-secret" \
user_alice="alice-secret";Client Configuration
Clients need corresponding configuration to authenticate to the broker:
bootstrap.servers=hostname:9093
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=PLAIN
sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required \
username="alice" \
password="alice-secret";Managing Kafka ACLs
Various tools are available for creating, listing, and deleting ACLs in Kafka.
Command-Line Tools
The primary tool for managing ACLs is the kafka-acls command-line interface:
kafka-acls --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--command-config admin-client.properties \
--add \
--allow-principal User:alice \
--operation Read \
--operation Write \
--topic ordersRedpanda provides rpk acl commands for similar functionality:
rpk acl create \
--allow-principal 'User:Charlie' \
--operation all \
--topic pingsConfluent Platform offers the confluent kafka acl command suite with additional capabilities.
GUI Tools
Conduktor provides a graphical interface for ACL management with views for visualizing relationships between principals and resources. It offers a wizard to simplify ACL creation based on common use cases and supports importing/exporting ACLs in CSV format.
Importing and Exporting ACLs
For managing ACLs at scale, tools like Kafka Security Manager (KSM) allow using external sources (like GitHub repositories) as the source of truth for ACLs. This provides auditability, rollback capabilities, and prevents unauthorized ACL modifications directly in Kafka.
Common Use Cases and ACL Patterns
Different scenarios require different ACL configurations:
Producer Access
To grant a user write access to a topic:
kafka-acls --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--add \
--allow-principal User:producer \
--operation Write \
--operation Create \
--operation Describe \
--topic ordersConsumer Access
To grant a user read access to a topic and consumer group:
kafka-acls --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--add \
--allow-principal User:consumer \
--operation Read \
--operation Describe \
--topic orders \
--group order-processorsAdmin Access
For administrative users who need cluster-wide permissions:
kafka-acls --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--add \
--allow-principal User:admin \
--operation All \
--clusterKRaft Mode Considerations
When using KRaft mode (ZooKeeper-less Kafka), some special considerations apply:
-
KRaft-backed clusters cannot use SCRAM for controller-to-controller authentication
-
SASL credentials should be created before brokers start running
-
For KRaft with SASL/PLAIN, you need the configuration property
sasl.mechanism.controller.protocol=PLAIN
Best Practices for Kafka ACLs
Implementing the following practices can enhance security and manageability:
Security Recommendations
-
Always use TLS with SASL to encrypt credentials in transit
-
Prefer SASL/SCRAM or SASL/GSSAPI over SASL/PLAIN in production environments
-
Implement proper credential management and rotation procedures
-
Configure ACLs with the principle of least privilege
-
Regularly audit and review ACL assignments
Mechanism Selection
Choose your SASL mechanism based on your existing infrastructure:

Avoiding Common Issues
-
Always use TLS with SASL/PLAIN to prevent credential exposure
-
Ensure correct JAAS configuration for each listener and mechanism
-
When using KRaft mode, set
super.userscorrectly to allow broker-to-controller communication -
Verify that client configurations match broker configurations for the selected mechanism
Troubleshooting Common ACL Issues
Common authorization and authentication issues include:
-
SaslAuthenticationException : Verify correct credentials and SASL mechanism configuration
-
SSL handshake failed : Check TLS certificates and truststore/keystore configuration
-
Could not find KafkaServer entry in JAAS configuration : Ensure proper JAAS configuration for controllers in KRaft mode
-
Unexpected Kafka request during SASL handshake : Verify client is properly configured for SASL authentication
Conclusion
Kafka ACLs provide a flexible and powerful mechanism for controlling access to your Kafka resources. By understanding the core concepts, implementing appropriate authentication mechanisms, and following best practices, you can create a secure and well-managed Kafka deployment that balances security needs with operational requirements.
Remember that ACLs are just one component of a comprehensive security strategy for Kafka. Combining ACLs with proper network security, TLS encryption, and secure credential management creates a defense-in-depth approach that effectively protects your Kafka infrastructure and data.
If you find this content helpful, you might also be interested in our product AutoMQ. AutoMQ is a cloud-native alternative to Kafka by decoupling durability to S3 and EBS. 10x Cost-Effective. No Cross-AZ Traffic Cost. Autoscale in seconds. Single-digit ms latency. AutoMQ now is source code available on github. Big Companies Worldwide are Using AutoMQ. Check the following case studies to learn more:
-
Grab: Driving Efficiency with AutoMQ in DataStreaming Platform
-
Palmpay Uses AutoMQ to Replace Kafka, Optimizing Costs by 50%+
-
How Asia’s Quora Zhihu uses AutoMQ to reduce Kafka cost and maintenance complexity
-
XPENG Motors Reduces Costs by 50%+ by Replacing Kafka with AutoMQ
-
Asia's GOAT, Poizon uses AutoMQ Kafka to build observability platform for massive data(30 GB/s)
-
AutoMQ Helps CaoCao Mobility Address Kafka Scalability During Holidays
-
JD.com x AutoMQ x CubeFS: A Cost-Effective Journey at Trillion-Scale Kafka Messaging