Apache Kafka Connect is a powerful framework for streaming data between Apache Kafka and external systems in a scalable, reliable manner. As organizations increasingly adopt real-time data processing, Kafka Connect has become a critical component for building data pipelines without writing custom code. This guide explores Kafka Connect's architecture, deployment models, configuration options, security considerations, and best practices.
What is Kafka Connect?
Kafka Connect is a framework and toolset for building and running data pipelines between Apache Kafka and other data systems. It provides a scalable and reliable way to move data in and out of Kafka, making it simple to quickly define connectors that move large data sets into Kafka (source connectors) or out of Kafka to external systems (sink connectors).
The framework offers several key benefits:
-
Data-centric pipeline : Connect uses meaningful data abstractions to pull or push data to Kafka
-
Flexibility and scalability : Connect runs with streaming and batch-oriented systems on a single node (standalone) or scaled to an organization-wide service (distributed)
-
Reusability and extensibility : Connect leverages existing connectors or extends them to fit specific needs, providing lower time to production
-
Simplified integration : Eliminates the need for custom code development for common integration scenarios
-
Centralized configuration management : Configuration is managed through simple JSON or properties files
Kafka Connect Architecture and Components
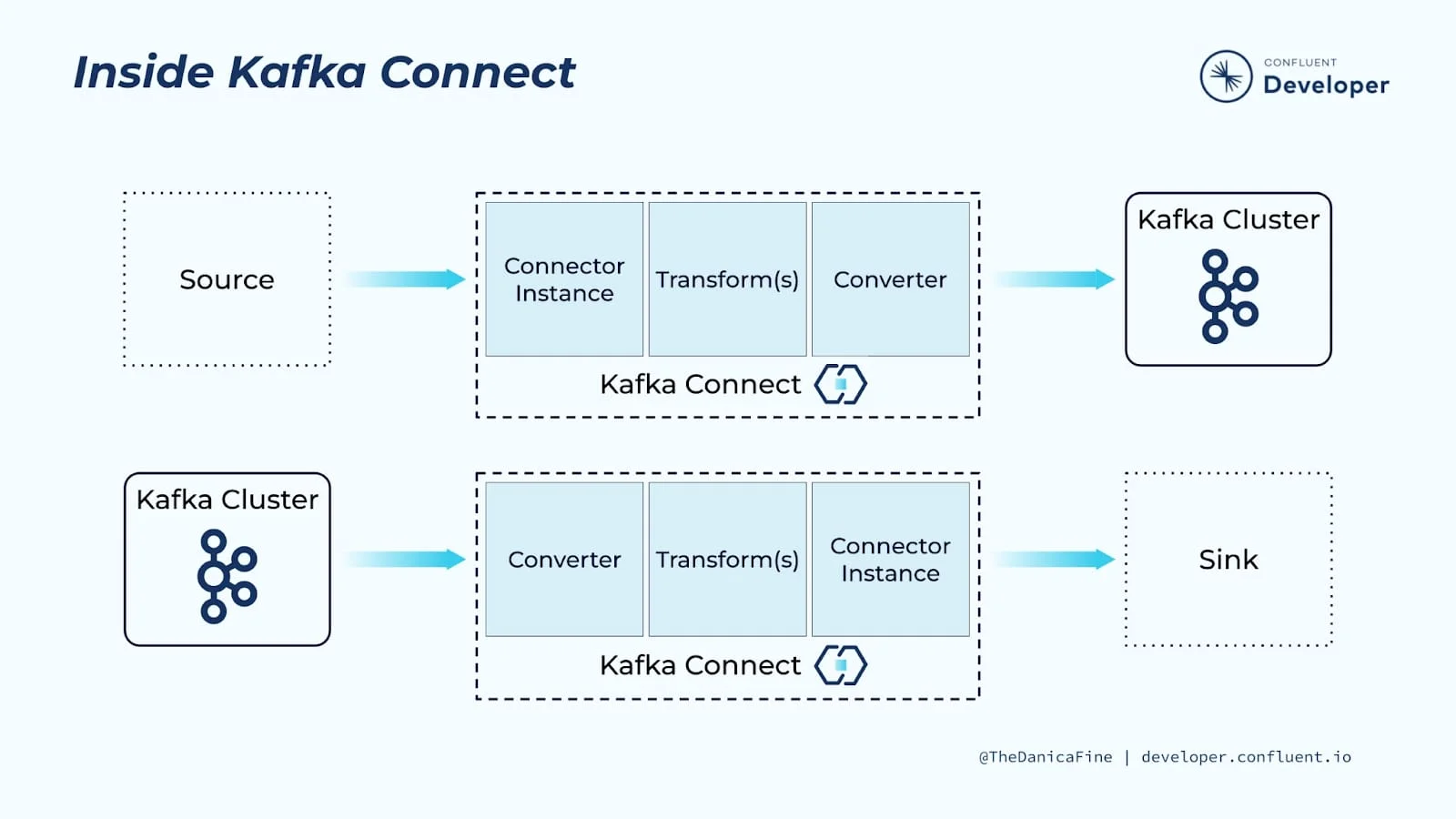
Kafka Connect follows a hierarchical architecture with several key components:
Core Components
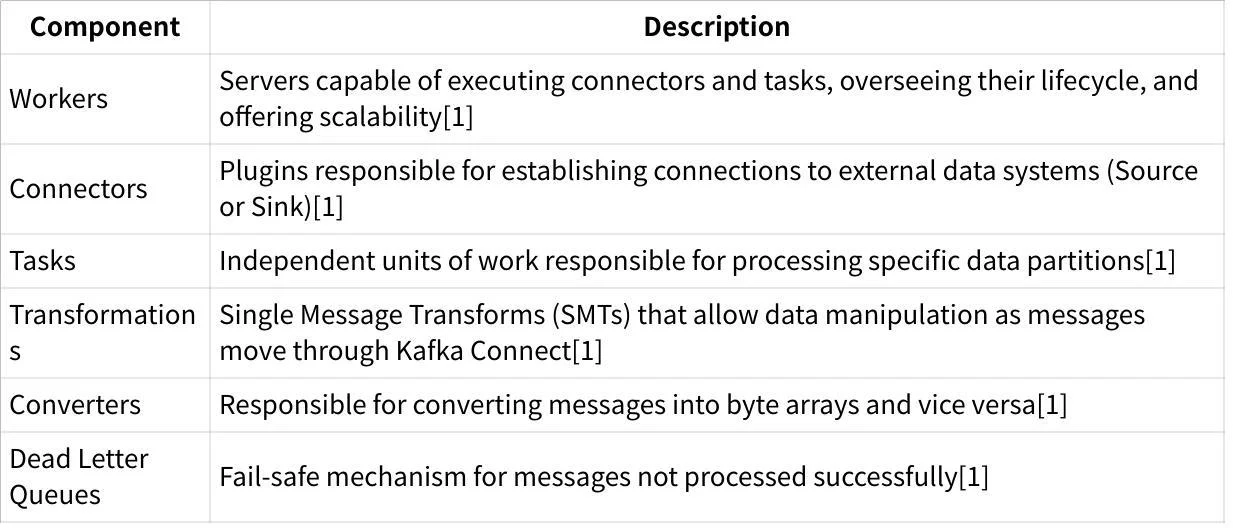
In Kafka Connect's architecture, connectors define how data is transferred, while tasks perform the actual data movement. Workers are the runtime environment that executes these connectors and tasks.
Deployment Models
Kafka Connect offers two deployment modes, each with its advantages:
Standalone Mode
Standalone mode is simpler but less resilient. It runs all workers, connectors, and tasks in a single process, making it suitable for development, testing, or smaller deployments.
Key characteristics:
-
Single process deployment
-
Configuration stored in properties files
-
Limited scalability and fault tolerance
-
Easier to set up and manage for development
Distributed Mode
Distributed mode is the recommended approach for production environments. It allows running Connect workers across multiple servers, providing scalability and fault tolerance.
Key characteristics:
-
Multiple worker processes across different servers
-
Configuration stored in Kafka topics
-
High scalability and fault tolerance
-
REST API for connector management
-
Internal topics (config, offset, status) store connector state
Connector Types
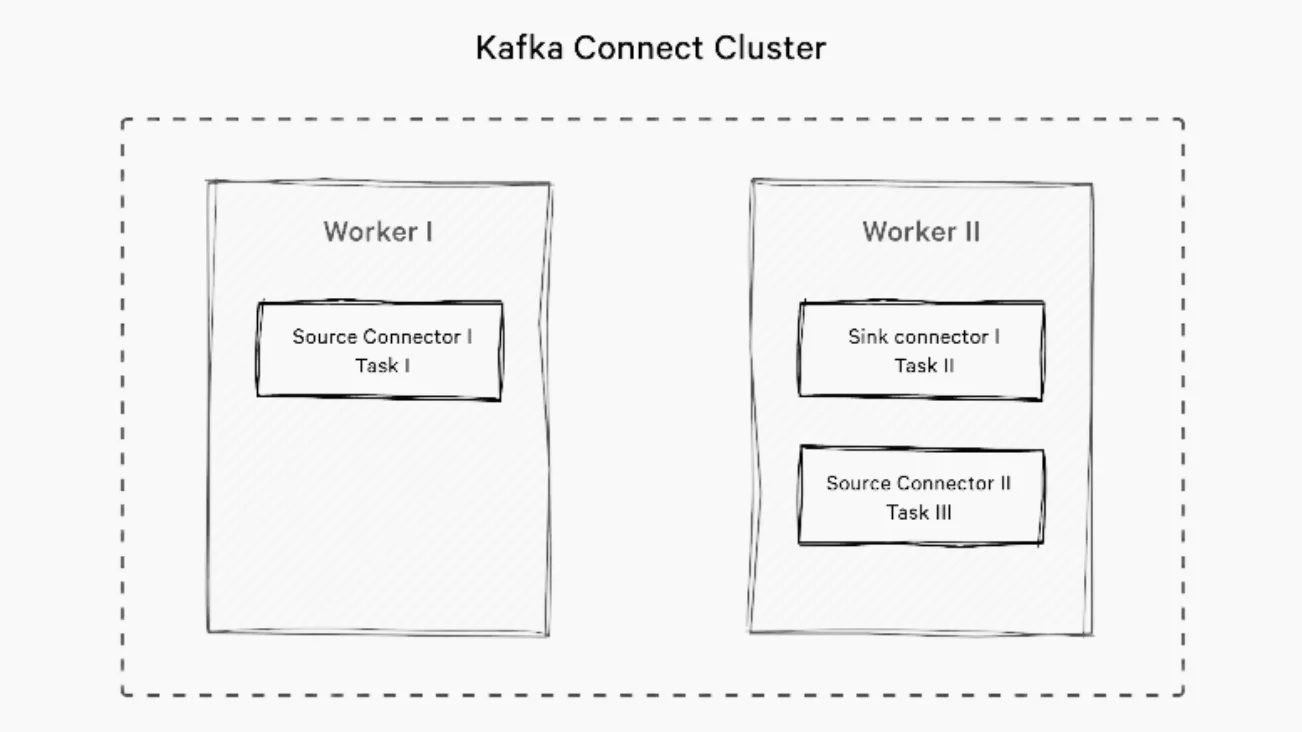
Source Connectors
Source connectors pull data from external systems and write it to Kafka topics. Examples include:
-
Database connectors (JDBC, MongoDB, MySQL)
-
File-based connectors (S3, HDFS)
-
Messaging system connectors (JMS, MQTT)
-
API-based connectors (Twitter, weather data)
Sink Connectors
Sink connectors read data from Kafka topics and push it to external systems. Examples include:
-
Database connectors (JDBC, Elasticsearch, MongoDB)
-
Cloud storage connectors (S3, GCS)
-
Data warehouse connectors (Snowflake, BigQuery)
-
Messaging system connectors (JMS, MQTT)
Configuration
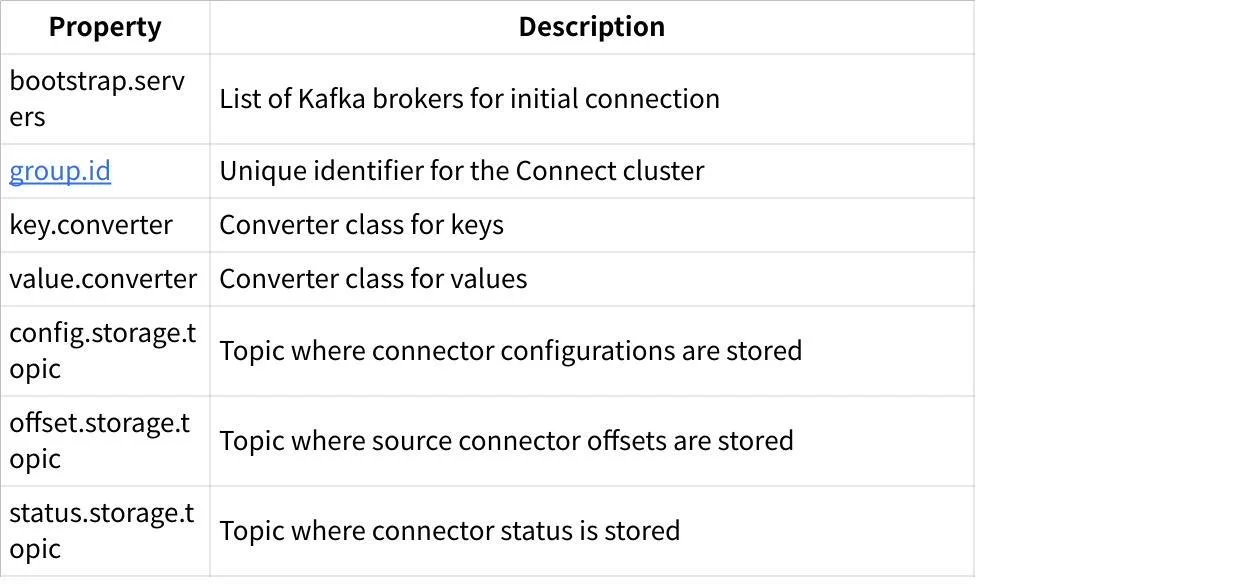
Worker Configuration
Worker configuration defines properties for the Kafka Connect runtime environment. Key properties include:
Connector Configuration
Connector configuration defines properties specific to each connector instance, typically provided in JSON format via the REST API. Common properties include:
-
connector.class: The Java class implementing the connector
-
tasks.max: Maximum number of tasks for this connector
-
topics/topics.regex: Topics to consume from (sink) or topic naming pattern (source)
-
Connector-specific configuration (connection URLs, credentials, etc.)
REST API
Kafka Connect provides a REST API for managing connectors. The API runs on port 8083 by default and offers endpoints for:
-
Listing, creating, updating, and deleting connectors
-
Viewing and modifying connector configurations
-
Checking connector and task status
-
Pausing, resuming, and restarting connectors
Example API usage:
# List all connectors
curl -s "http://localhost:8083/connectors"
# Get connector status
curl -s "http://localhost:8083/connectors/[connector-name]/status"Single Message Transforms (SMTs)
SMTs allow manipulation of individual messages as they flow through Connect. They can be used to:
-
Filter messages
-
Modify field values
-
Add or remove fields
-
Change message routing
-
Convert between formats
Multiple transformations can be chained together to form a processing pipeline.
Security Considerations
Authentication and Encryption
If Kafka uses authentication or encryption, Kafka Connect must be configured accordingly:
-
TLS/SSL for encryption
-
SASL for authentication (PLAIN, SCRAM, Kerberos)
-
ACLs for authorization
Connector Security
Connectors often require credentials to access external systems. Kafka Connect offers several approaches:
-
Secrets storage for sensitive configuration data
-
Separate service principals for connectors
-
Integration with external secret management systems
Network Security
Restrict access to the Kafka Connect REST API using network policies and firewalls, as it doesn't support authentication by default.
Monitoring and Management
Effective monitoring is crucial for Kafka Connect operations:
Metrics to Monitor

Monitoring Tools
Several tools can help monitor Kafka Connect:
-
Confluent Control Center or Confluent Cloud
-
Conduktor
-
JMX monitoring via Prometheus and Grafana
-
Custom solutions using the Connect REST API
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Common Problems
-
Consumer Lag : Consumers falling behind producers, causing delays in data processing
-
Connector Failures : Connectors stopping due to configuration issues or external system unavailability
-
Rebalancing Issues : Frequent rebalancing causing disruptions
-
Task Failures : Individual tasks failing due to data issues or resource constraints
-
Network Issues : Connection problems between Kafka Connect and external systems
Troubleshooting Approaches
-
Check connector and task status via REST API
-
Examine the Kafka Connect log files
-
Monitor connector metrics
-
Inspect dead letter queues for failed messages
-
Review configuration for errors or misconfigurations
Best Practices
Performance Optimization
-
Tune tasks.max : Match the number of tasks to the number of partitions or processing capability
-
Configure batch sizes : Adjust batch sizes for optimal throughput
-
Monitor resource usage : Ensure workers have sufficient CPU, memory, and network resources
-
Use appropriate converters : Choose efficient converters for your data format
Deployment Recommendations
-
Use distributed mode for production : Provides scalability and fault tolerance
-
Deploy dedicated Connect clusters : Separate from Kafka brokers for independent scaling
-
Implement proper monitoring : Set up alerts for connector failures and performance issues
-
Use dead letter queues : Capture messages that fail processing
Connector Management
-
Version control configurations : Store connector configurations in version control
-
Follow progressive deployment : Test connectors in development environments before production
-
Document connector configurations : Maintain documentation for all deployed connectors
-
Implement CI/CD pipelines : Automate connector deployment and testing
Use Cases
Kafka Connect is widely used in various scenarios:
Data Integration
-
Change Data Capture (CDC) : Capturing database changes in real-time
-
ETL Processes : Extracting, transforming, and loading data between systems
-
Log Aggregation : Consolidating logs from multiple sources
Cloud Migration
-
Hybrid Cloud Solutions : Bridging on-premises and cloud environments
-
Multi-Cloud Integration : Connecting data across different cloud providers
Real-time Analytics
-
Event Streaming : Moving event data to analytics platforms
-
Metrics Collection : Gathering metrics for monitoring and analysis
-
Real-time Dashboards : Feeding data to visualization tools
Conclusion
Kafka Connect has become an essential tool for building data pipelines and integrating Apache Kafka with external systems. Its plugin architecture, scalability, and ease of use make it valuable for organizations looking to implement real-time data streaming solutions without writing custom code.
By understanding Kafka Connect's architecture, deployment options, configuration, and best practices, organizations can effectively implement and maintain robust data pipelines that meet their business needs. Whether used for change data capture, log collection, cloud integration, or analytics, Kafka Connect provides a standardized approach to data integration that leverages the power and reliability of Apache Kafka.
If you find this content helpful, you might also be interested in our product AutoMQ. AutoMQ is a cloud-native alternative to Kafka by decoupling durability to S3 and EBS. 10x Cost-Effective. No Cross-AZ Traffic Cost. Autoscale in seconds. Single-digit ms latency. AutoMQ now is source code available on github. Big Companies Worldwide are Using AutoMQ. Check the following case studies to learn more:
-
Grab: Driving Efficiency with AutoMQ in DataStreaming Platform
-
Palmpay Uses AutoMQ to Replace Kafka, Optimizing Costs by 50%+
-
How Asia’s Quora Zhihu uses AutoMQ to reduce Kafka cost and maintenance complexity
-
XPENG Motors Reduces Costs by 50%+ by Replacing Kafka with AutoMQ
-
Asia's GOAT, Poizon uses AutoMQ Kafka to build observability platform for massive data(30 GB/s)
-
AutoMQ Helps CaoCao Mobility Address Kafka Scalability During Holidays