Deploying Apache Kafka on Kubernetes can be streamlined significantly through Helm charts, which package all the necessary Kubernetes resources into reusable templates. This comprehensive guide explores the landscape of Kafka Helm charts, including options from major providers, installation procedures, configuration options, and best practices for production deployments.
Understanding Kafka Helm Charts and Deployment Options
Helm serves as a package manager for Kubernetes, similar to apt for Linux or Brew for macOS. Helm charts contain pre-configured Kubernetes resources (Deployments, Services, StatefulSets, etc.) needed to deploy applications like Kafka on Kubernetes. For those deploying Kafka on Kubernetes, two primary approaches exist: Helm charts and Kubernetes operators.
Helm Charts vs. Operators
Helm charts provide a simpler, more flexible approach for deploying Kafka. You control Kafka through Helm commands and must handle day-to-day operations yourself. This offers considerable freedom in configuration but requires more manual management.
Operators, on the other hand, implement the Kubernetes operator pattern and provide more sophisticated automation. They not only handle installation but also manage day-2 operations like scaling, updates, and failures. As explained by Datadog, "Operators provide a more sophisticated and automated approach to managing applications by applying operational knowledge throughout their lifetime".
The choice between them depends on your specific needs:
-
Helm charts are best for simple deployments where you need flexibility and are comfortable managing Kafka
-
Operators are ideal for complex environments requiring automated management and custom lifecycle operations
Major Kafka Helm Chart Providers
Confluent Platform Helm Charts
Confluent, the company founded by Kafka's creators, offers Helm charts for deploying Confluent Platform components on Kubernetes. These charts enable developers to quickly provision Apache Kafka, ZooKeeper, Schema Registry, REST Proxy, and Kafka Connect.
Note that the original cp-helm-charts repository is now deprecated in favor of Confluent for Kubernetes (CFK), their Kubernetes operator solution. The original charts were designed for development, test, and proof of concept environments.
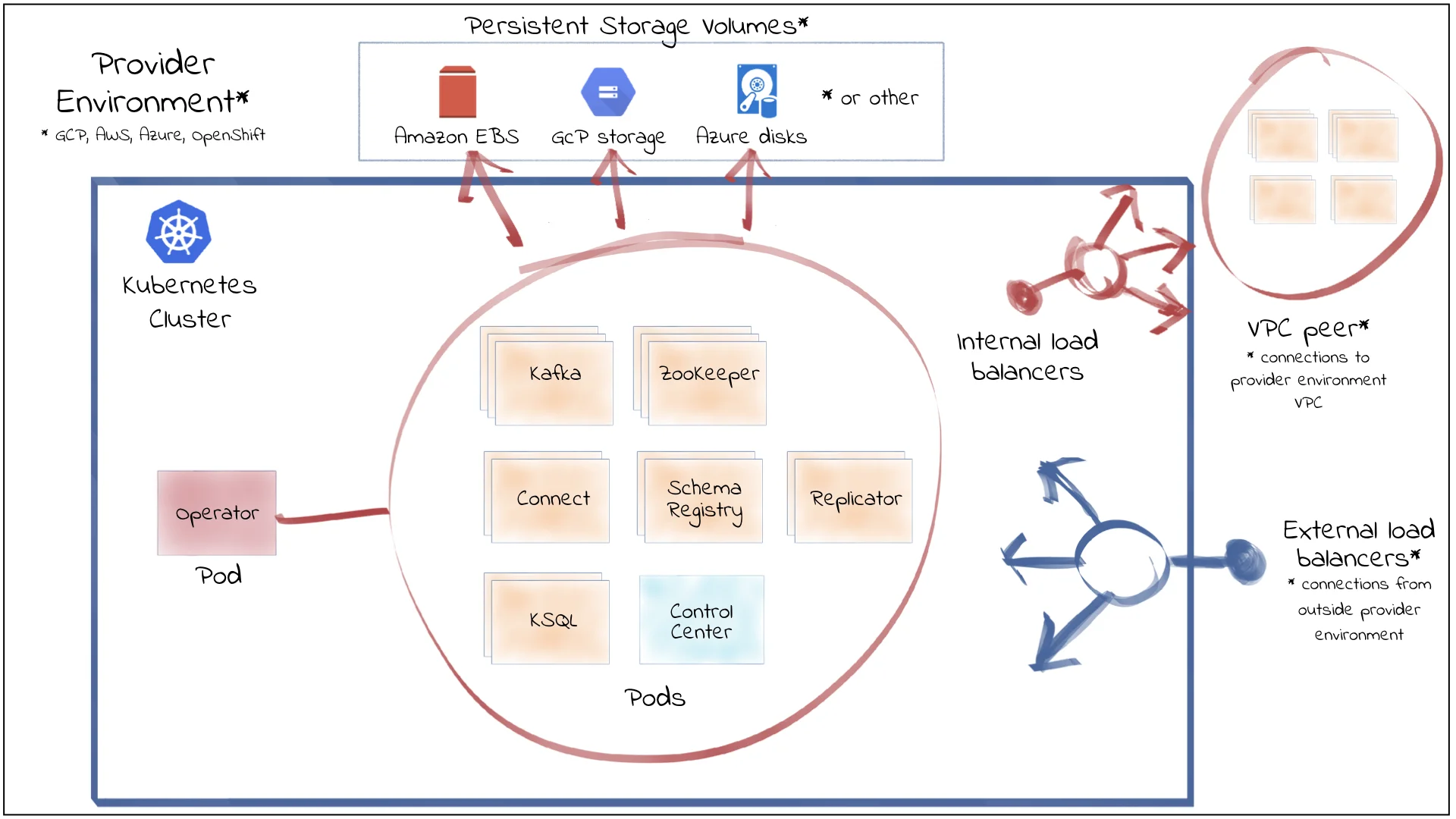
Bitnami Kafka Helm Chart
Bitnami offers a well-maintained Kafka Helm chart that follows best practices for security, efficiency, and performance. It provides comprehensive configuration options for credentials management, persistence settings, and cluster deployment.
Downloading and Installing Kafka Helm Charts
Adding Repositories and Basic Installation
For most Kafka Helm charts, the installation process follows a similar pattern:
-
Add the chart repository to your Helm configuration
-
Update repositories
-
Install the chart with desired configurations
Confluent Platform Example:
helm repo add confluentinc <https://confluentinc.github.io/cp-helm-charts/> helm repo update helm install my-confluent confluentinc/cp-helm-charts --version 0.6.0Note that this installs the deprecated chart version. For new deployments, Confluent recommends using their Kubernetes operator.
Bitnami Example:
To install Kafka using the Bitnami Helm chart, follow these steps:
- Add the Bitnami Helm Repository :
helm repo add bitnami <https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami>- Update Helm Repositories :
helm repo update- Install the Kafka Chart :
helm install my-kafka bitnami/kafkaYou can customize the installation by specifying additional parameters. For example, to enable external access via a NodePort service:
helm install kafka bitnami/kafka \
--set externalAccess.enabled=true \
--set externalAccess.controller.service.type=NodePort \
--set externalAccess.controller.service.ports.external=9094This command installs Kafka with external access enabled and exposes the Kafka service on port 9094.
Common Configurations and Customizations
Persistence Configuration
Persistence configuration is crucial for Kafka deployments. Most Helm charts allow configuring:
-
Storage class
-
Volume size
-
Retention policies
In Bitnami's chart, for example, you'll encounter issues if you don't properly manage storage persistence. The chart typically creates PersistentVolumeClaims (PVCs) that remain even after uninstalling the chart.
External Access Configuration
Providing external access to Kafka requires specific configuration. In the Redpanda Helm chart, you can set external.type to either "NodePort" or "LoadBalancer" depending on your infrastructure needs.
ZooKeeper Configuration
Many Kafka charts deploy ZooKeeper by default, but allow disabling it if you want to use an existing ZooKeeper ensemble:
helm install kafka rhcharts/kafka --set zookeeper.enabled=false --set zookeeper.url="your-zookeeper:2181"Broker Configuration
You can customize broker settings through the values file. Common configurations include:
-
Replica count
-
Resource limits (CPU, memory)
-
Log retention policies
-
Authentication settings
Best Practices for Kafka Helm Chart Deployment
Using Separated Storage and Compute in Kafka for Better Operations and Scaling
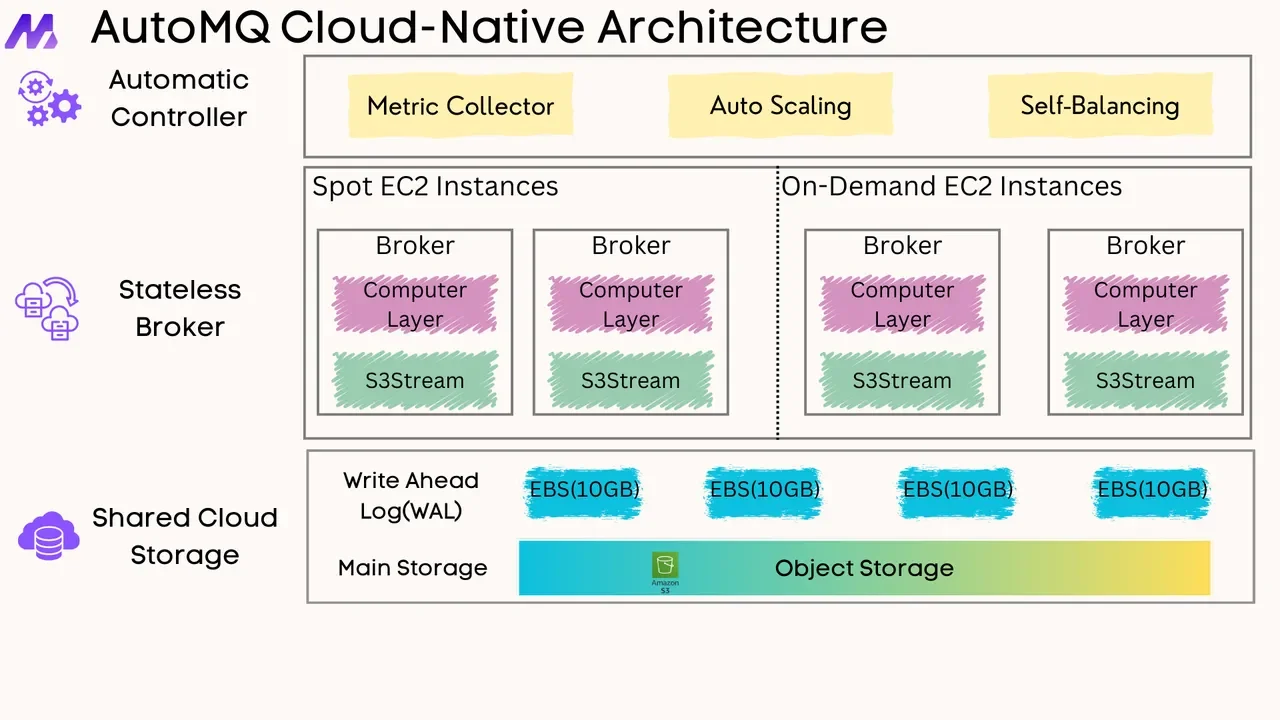
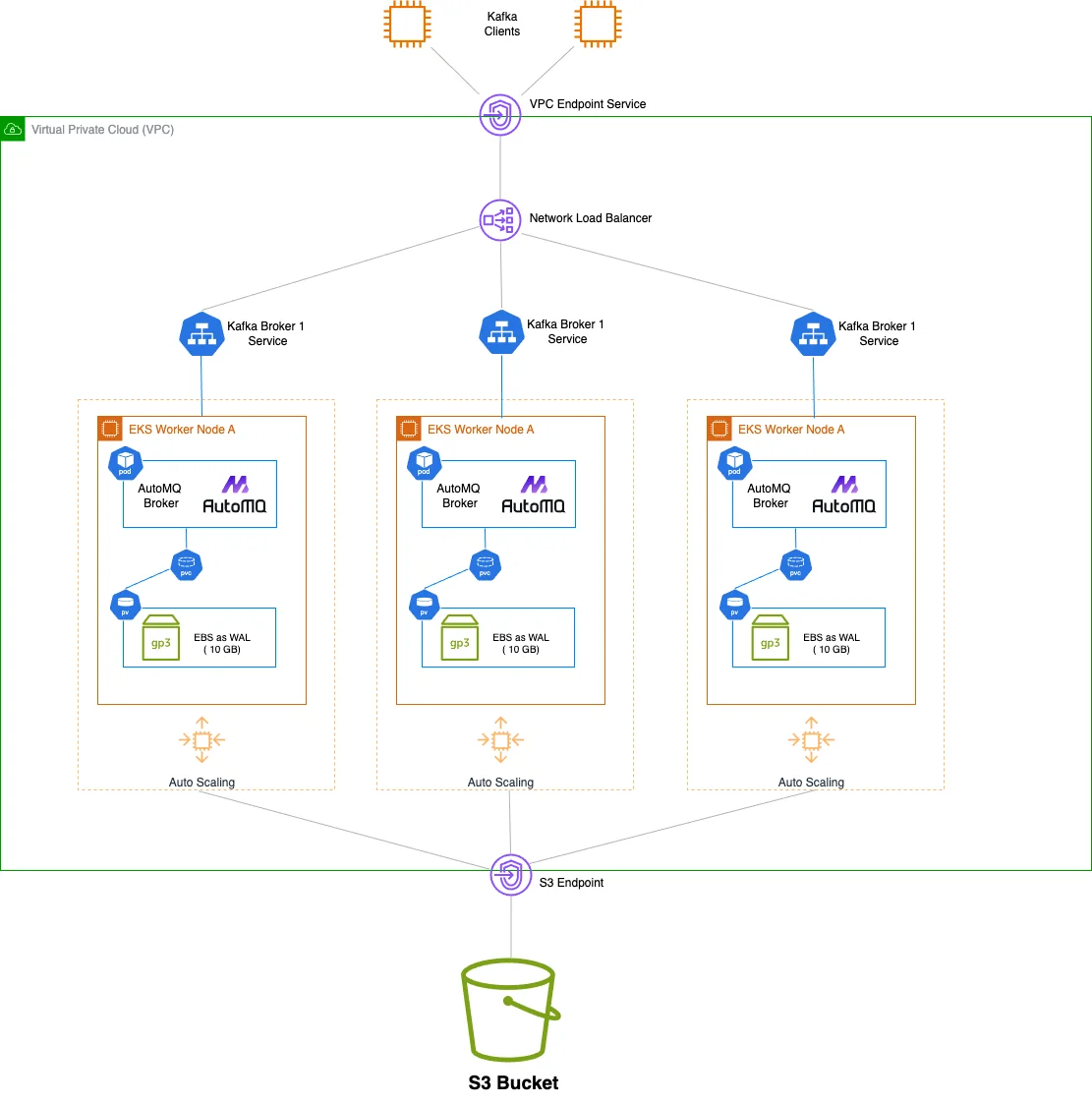
Kubernetes is primarily designed for cloud-native stateless applications. The main challenge of running Kafka on Kubernetes lies in its architecture that couples compute and storage, with strong dependency on local disks. This makes Kafka difficult to manage and scale on Kubernetes. With the continuous evolution of the Kafka ecosystem, you can now choose next-generation storage-compute separated Kafka solutions like AutoMQ. AutoMQ is built entirely on S3, with complete separation of compute and storage. The stateless Broker significantly reduces the management complexity of Kafka on Kubernetes.
Topic Configuration
For optimal Kafka performance, consider these topic best practices:
-
Partition Replication : Maintain 2+ replicas for each partition to ensure fault tolerance
-
Partition Count : Keep total partitions for a topic below 10 and cluster-wide below 10,000
-
Message Size Control : Messages should not exceed 1GB to avoid increased seek time
-
Mission-Critical Topics : Isolate high-throughput topics to the most performant brokers
-
Cleanup Policy : Establish clear policies for deleting unused topics
Resource Allocation
Properly allocate resources to ensure Kafka performs optimally:
-
CPU and Memory : Allocate sufficient resources based on expected throughput
-
Storage : Provision adequate persistent storage for logs and data
-
Network : Ensure network policies allow required communication
Monitoring and Metrics
Most Kafka charts support exposing metrics for monitoring. For example, the Conduktor Helm chart includes options for Prometheus metrics integration:
textmetrics:
enabled: true
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
interval: 30sThis configuration creates a ServiceMonitor resource for Prometheus to scrape metrics from Conduktor.
Upgrade Considerations
When upgrading Kafka versions through Helm, follow a staged approach as demonstrated in Axual's documentation:
-
Update configuration values first
-
Perform the Helm upgrade
-
Verify services are running correctly before proceeding
-
For major version upgrades, consider updating inter-broker protocol version in a separate step
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Persistence and Storage Issues
Storage issues are among the most common problems with Kafka on Kubernetes. If you're experiencing issues with the Bitnami Kafka chart:
-
Check storage provisioning and ensure PVCs are correctly bound
-
Monitor disk usage to avoid running out of space
-
Consider implementing proper log retention policies
-
For log persistence, use the
logPersistence.sizeparameter to adjust the volume size
Configuration Errors During Upgrades
When upgrading Helm chart releases with stateful applications like Kafka, credential errors can occur if you relied on Helm to generate random passwords. Best practices include:
-
Explicitly setting credentials in your values file
-
Using existing Secrets (created before installation)
-
Never relying on random generation for production environments
Scaling and Performance Problems
If experiencing performance issues:
-
Check broker resource utilization
-
Monitor network throughput
-
Analyze topic partitioning strategy
-
Consider using a Kafka operator for complex scaling scenarios
Debugging Tools
For troubleshooting Kafka issues, consider deploying auxiliary tools:
Kafkacat for Event Viewing
The OpenCORD guide suggests deploying a kafkacat container for diagnostic purposes:
helm install -n kafkacat cord/kafkacatOnce deployed, you can exec into the pod to run commands like:
kafkacat -b kafka -L # List topics kafkacat -b kafka -C -t your-topic # Listen for eventsThis helps in debugging Kafka event flow issues.
Conclusion
Helm charts provide a powerful way to deploy and manage Kafka on Kubernetes, offering flexibility and consistency across environments. While several options exist—from Confluent's platform to Bitnami's chart to newer alternatives like Redpanda—the choice depends on your specific requirements and comfort with Kubernetes operations.
For simpler deployments where customization is important, Helm charts offer an excellent solution. For complex, production-grade deployments requiring sophisticated automation, consider Kubernetes operators like Confluent for Kubernetes or Strimzi.
Regardless of your choice, following best practices for topic configuration, resource allocation, and monitoring will help ensure a stable, performant Kafka deployment on Kubernetes. Always consider your specific use case, expected throughput, and operational capabilities when choosing between deployment options.
If you find this content helpful, you might also be interested in our product AutoMQ. AutoMQ is a cloud-native alternative to Kafka by decoupling durability to S3 and EBS. 10x Cost-Effective. No Cross-AZ Traffic Cost. Autoscale in seconds. Single-digit ms latency. AutoMQ now is source code available on github. Big Companies Worldwide are Using AutoMQ. Check the following case studies to learn more:
-
Grab: Driving Efficiency with AutoMQ in DataStreaming Platform
-
Palmpay Uses AutoMQ to Replace Kafka, Optimizing Costs by 50%+
-
How Asia’s Quora Zhihu uses AutoMQ to reduce Kafka cost and maintenance complexity
-
XPENG Motors Reduces Costs by 50%+ by Replacing Kafka with AutoMQ
-
Asia's GOAT, Poizon uses AutoMQ Kafka to build observability platform for massive data(30 GB/s)
-
AutoMQ Helps CaoCao Mobility Address Kafka Scalability During Holidays
-
JD.com x AutoMQ x CubeFS: A Cost-Effective Journey at Trillion-Scale Kafka Messaging