Overview
SAML-based Single Sign-On (SSO) integration with Kafka ecosystems has become increasingly important as organizations seek to standardize authentication across their enterprise applications. This comprehensive guide explores how to implement, configure, and troubleshoot SAML SSO with Kafka management tools and services, providing a security layer that leverages your existing identity infrastructure.
Understanding Kafka Authentication and SAML SSO
Kafka itself traditionally uses SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer) mechanisms for authentication, while SAML SSO is typically implemented at the management tool or UI layer that interacts with Kafka. This architectural separation is important to understand when planning your implementation.
What is SAML SSO?
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an XML-based framework for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties. Single Sign-On enables users to access multiple applications with one set of credentials13.
There are two primary SSO types:
Enterprise login : Allows users to connect to applications using company credentials
Social login : Enables access via Google, Facebook, or other social accounts6
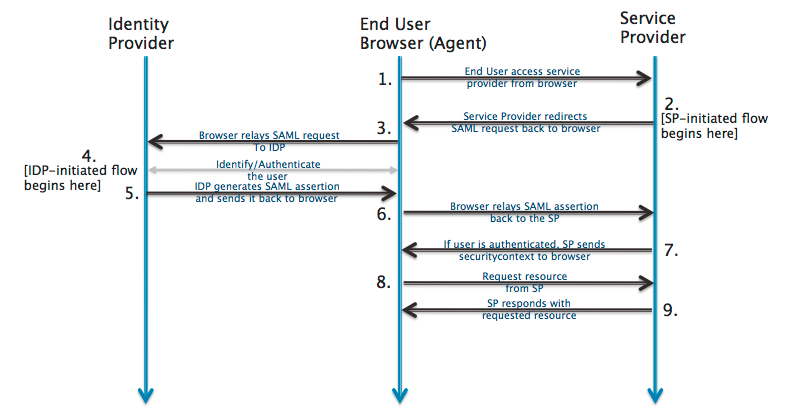
Authentication Flow
The typical SAML authentication flow with Kafka tools involves:
User attempts to access a Kafka management interface
Service redirects to the configured Identity Provider (IdP)
User authenticates with corporate credentials at the IdP
IdP generates a SAML assertion containing the user's identity
This assertion is sent back to the service provider
Service validates the assertion and grants access to Kafka resources
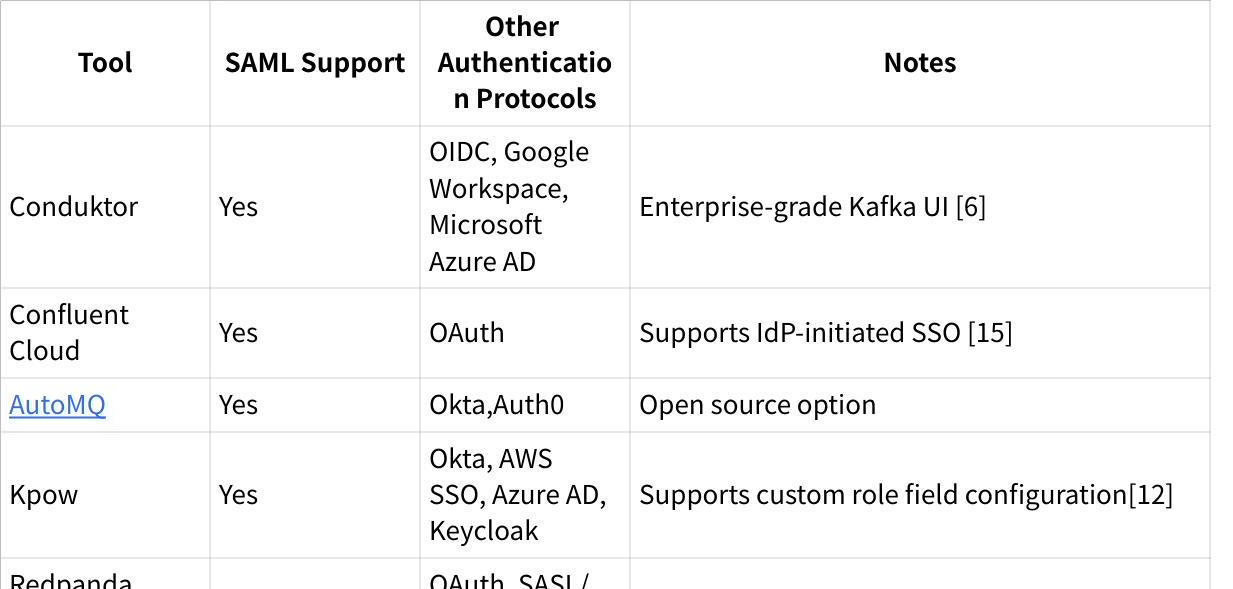
Supported Kafka Management Tools with SAML SSO
Several popular Kafka management tools support SAML SSO integration:
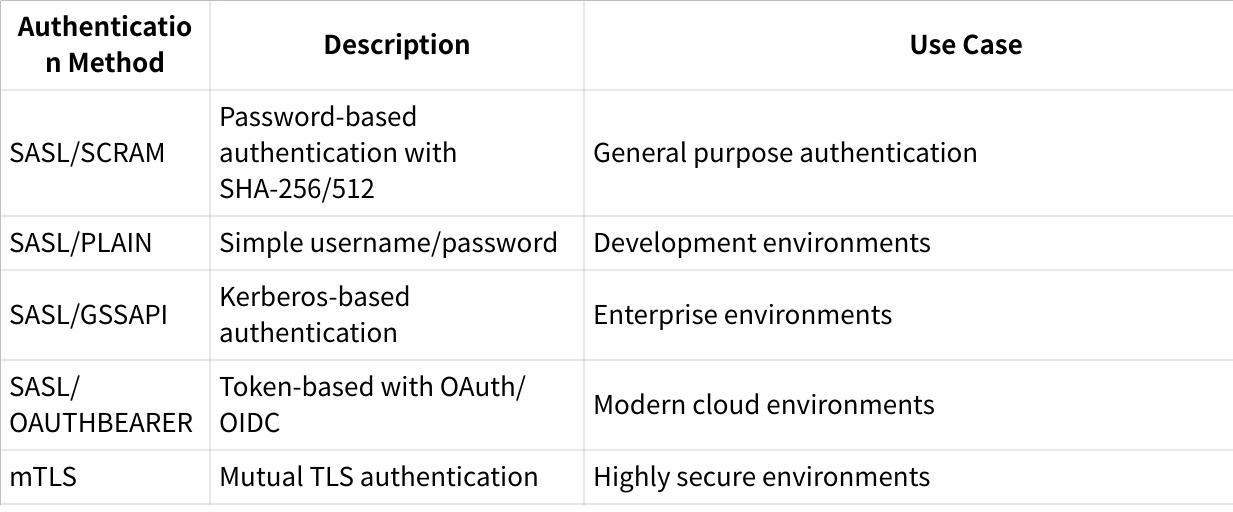
Kafka Broker Authentication Methods
While SAML SSO provides access to management tools, these tools still need to authenticate with Kafka brokers. Common authentication methods include:
SAML Security Best Practices
When implementing SAML SSO with Kafka tools, follow these best practices:
Communication Security :
Use TLS v1.2 or higher when connecting to service providers
Avoid SSL v2, SSL v3, and TLS v1 as they are insecure
Communicate only with service providers using SHA-2 certificates[13]
Certificate Management :
Use only SHA-2 certificates for new SAML workflows
Replace SHA-1 certificates with SHA-2 at earliest opportunity
Avoid self-signed certificates - use certificates from trusted PKI CA[13]
Identity Management :
Implement proper RBAC for Kafka resource access
Forward company groups to Kafka management tools
Configure automatic account disabling when users leave the company[6]
Session Management :
Set appropriate session timeouts (default is typically 1 hour)
Consider implementing network-based restrictions for access12
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Authentication Failures
When troubleshooting SAML authentication issues:
Enable debugging in your Kafka management tool
For Kpow:
DEBUG_AUTH=true12Check SAML response payloads using tools like samltool.com
Verify connection parameters
Entity ID/Audience URI matches between IdP and SP
ACS URL is correctly configured
Certificate fingerprints match
Check SAML assertions
Ensure required attributes/claims are present
Verify mapping of roles/groups
Conclusion
Implementing SAML SSO with Kafka management tools provides a seamless authentication experience while maintaining enterprise security standards. While Kafka brokers themselves typically use SASL authentication mechanisms, the management layer can leverage SAML to integrate with your existing identity infrastructure.
By following the configurations outlined for tools like Conduktor, Confluent Cloud, Kpow, and others, you can successfully implement SAML SSO for your Kafka ecosystem. Always adhere to security best practices and thoroughly test your implementation to ensure both security and usability requirements are met.
Remember that specific steps may vary based on your chosen IdP and Kafka management tools, so always refer to the latest documentation for your specific versions.
If you find this content helpful, you might also be interested in our product AutoMQ. AutoMQ is a cloud-native alternative to Kafka by decoupling durability to S3 and EBS. 10x Cost-Effective. No Cross-AZ Traffic Cost. Autoscale in seconds. Single-digit ms latency. AutoMQ now is source code available on github. Big Companies Worldwide are Using AutoMQ. Check the following case studies to learn more:
Grab: Driving Efficiency with AutoMQ in DataStreaming Platform
Palmpay Uses AutoMQ to Replace Kafka, Optimizing Costs by 50%+
How Asia’s Quora Zhihu uses AutoMQ to reduce Kafka cost and maintenance complexity
XPENG Motors Reduces Costs by 50%+ by Replacing Kafka with AutoMQ
Asia's GOAT, Poizon uses AutoMQ Kafka to build observability platform for massive data(30 GB/s)
AutoMQ Helps CaoCao Mobility Address Kafka Scalability During Holidays
JD.comx AutoMQ x CubeFS: A Cost-Effective Journey at Trillion-Scale Kafka Messaging













.png)