SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer) authentication provides robust security mechanisms for Apache Kafka clusters, enabling secure communication between clients and brokers. This comprehensive guide explores SASL authentication in Kafka, including its mechanisms, implementation details, configuration options, and best practices for production environments.
Understanding SASL Authentication in Kafka
SASL is a framework that provides authentication and data security in network protocols. In Kafka, SASL is used to authenticate clients (producers and consumers) and brokers using various mechanisms. Each mechanism offers different security features and complexity levels, allowing organizations to choose the one that best fits their requirements.
Key Concepts
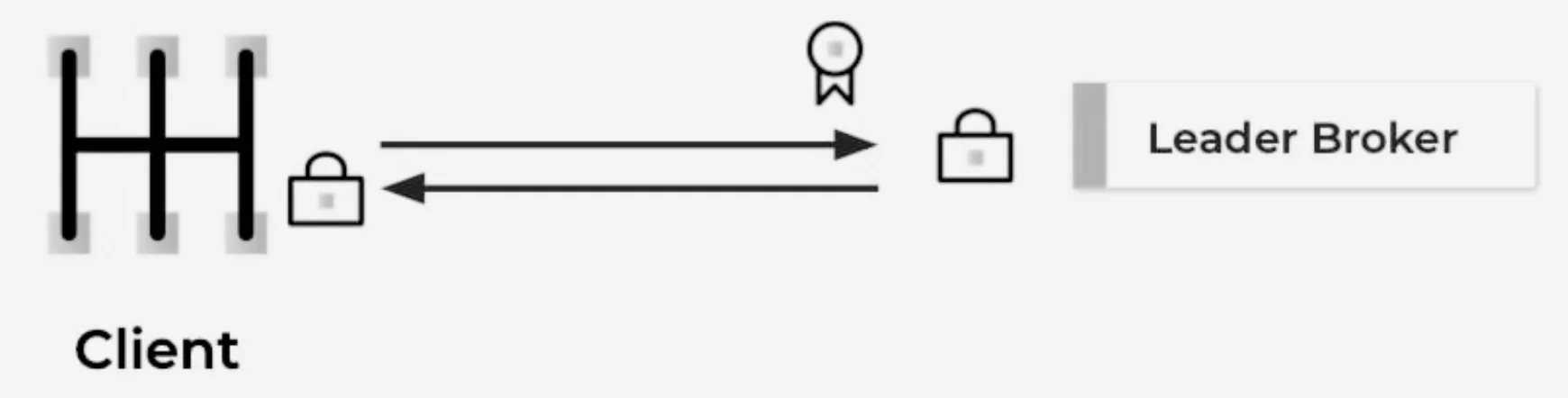
KafkaPrincipal represents the identity of a user or service interacting with the Kafka cluster. When clients attempt to connect, they present their KafkaPrincipal, which Kafka verifies before allowing access to resources. This principal is then used for subsequent authorization checks through Access Control Lists (ACLs).
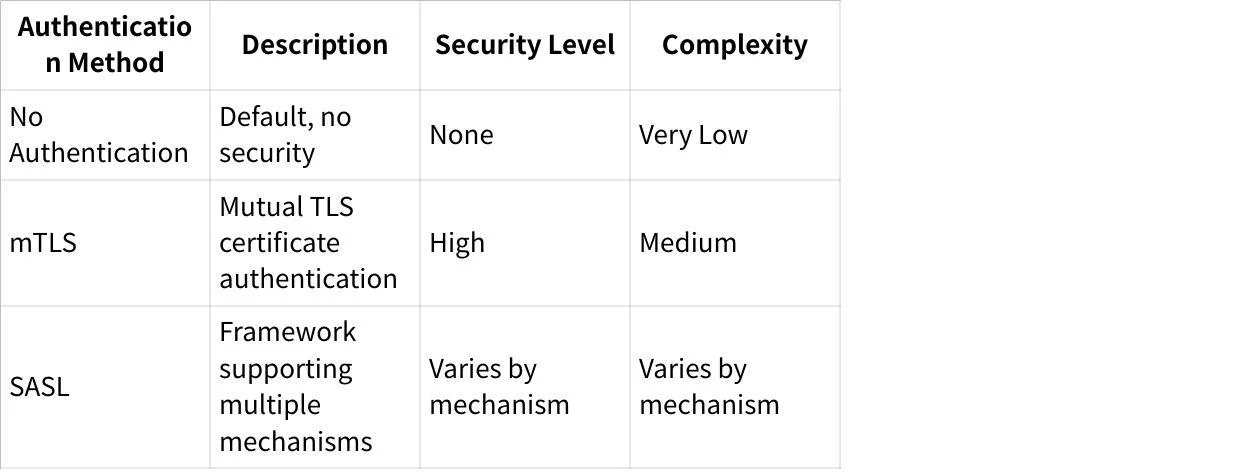
SASL vs. Other Authentication Methods
Kafka supports multiple authentication methods:
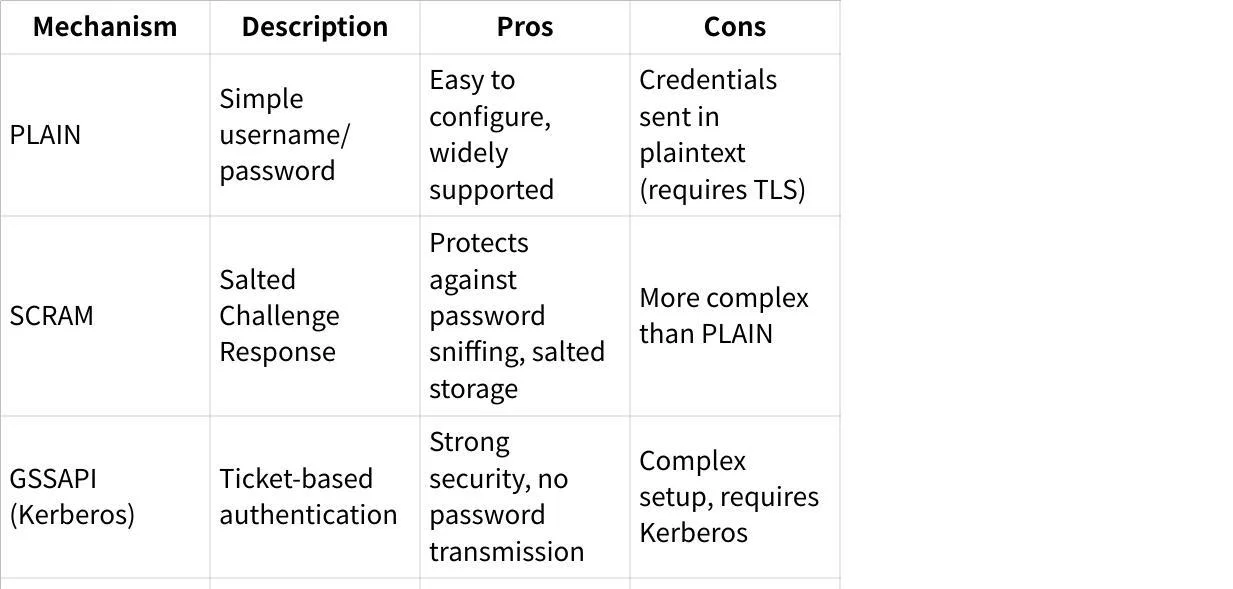
SASL Mechanisms Supported by Kafka
Kafka supports several SASL mechanisms, each with distinct characteristics:
SASL Authentication Mechanisms in Detail
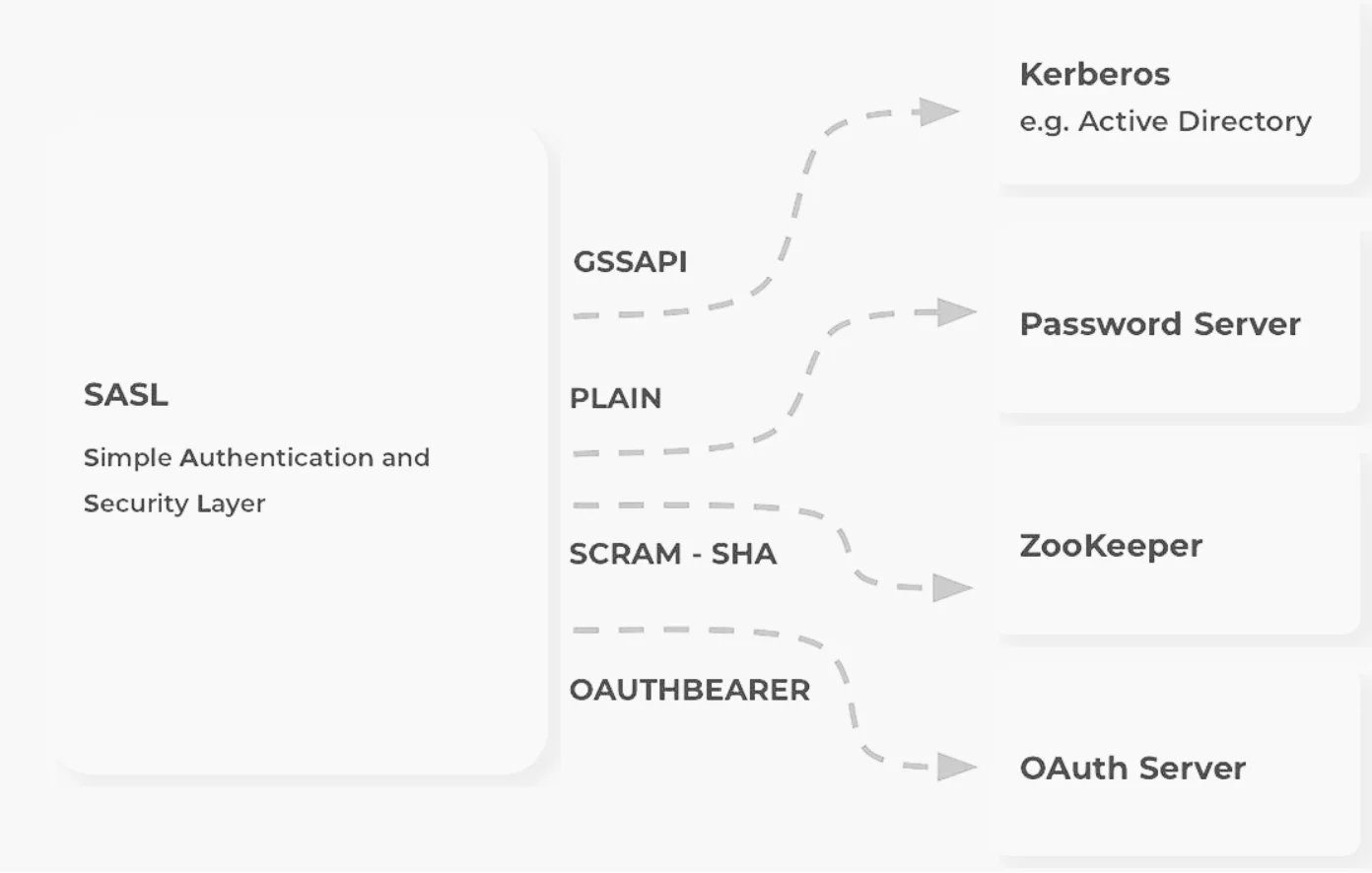
SASL/PLAIN
SASL/PLAIN is a simple username/password authentication mechanism. While straightforward to implement, it transmits credentials in plaintext, making it vulnerable if not used with TLS encryption.
PLAIN should not be confused with PLAINTEXT, which refers to the absence of transport encryption. Configuration parameters such as sasl.enabled.mechanisms may be set to use the SASL mechanism PLAIN, whereas parameters like security.inter.broker.protocol may be configured to use SASL_PLAINTEXT (SASL authentication without encryption) or SASL_SSL (SASL authentication with TLS encryption).
SASL/SCRAM
SCRAM (Salted Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism) addresses security concerns with traditional mechanisms like PLAIN by:
-
Protecting against password sniffing on networks
-
Preventing dictionary attacks on password files
-
Storing authentication information in salted form to protect against database compromises
Confluent Platform supports both SCRAM-SHA-256 and SCRAM-SHA-512 variants, storing credentials in KRaft or ZooKeeper.
SASL/GSSAPI (Kerberos)
GSSAPI with Kerberos provides ticket-based authentication, eliminating the need to transmit passwords. It requires a functioning Kerberos infrastructure and is more complex to set up but offers strong security guarantees.
SASL/OAUTHBEARER
OAUTHBEARER leverages OAuth tokens for authentication, allowing integration with external identity providers. Users must provide custom code to acquire and verify credentials.
How SASL Authentication Works in Kafka
The SASL authentication process follows these general steps:
-
Client initiates connection to Kafka broker
-
Broker responds with supported SASL mechanisms
-
Client selects a mechanism and begins authentication handshake
-
Credentials are exchanged according to the mechanism's protocol
-
Broker verifies credentials and either allows or denies the connection
-
If successful, the client's KafkaPrincipal is used for subsequent authorization
Configuring SASL Authentication
JAAS Configuration
Kafka uses the Java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS) for SASL configuration. There are two approaches to configuring JAAS:
-
Using the
sasl.jaas.configproperty (recommended) -
Passing a JAAS configuration file via the
java.security.auth.login.configsystem property
For brokers, JAAS configuration should be prefixed with the listener name and SASL mechanism:
listener.name.<listenerName>.<saslMechanism>.sasl.jaas.config
Broker Configuration
The following example shows a broker configuration for SASL/PLAIN:
# Enable SASL mechanisms
sasl.enabled.mechanisms=PLAIN
# Configure security protocol
listeners=SASL_SSL://hostname:9093
advertised.listeners=SASL_SSL://hostname:9093
security.inter.broker.protocol=SASL_SSL
# Set mechanism for inter-broker communication
sasl.mechanism.inter.broker.protocol=PLAIN
# JAAS configuration for the listener
listener.name.sasl_ssl.plain.sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required \
username="admin" \
password="admin-secret" \
user_admin="admin-secret" \
user_alice="alice-secret";
Client Configuration
For clients, you can embed JAAS configuration directly in the properties:
bootstrap.servers=hostname:9093
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=PLAIN
sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required \
username="alice" \
password="alice-secret";
Enabling Multiple SASL Mechanisms
Kafka brokers can support multiple SASL mechanisms simultaneously, while each client must choose one. Configure each mechanism with its own JAAS configuration:
sasl.enabled.mechanisms=SCRAM-SHA-512,GSSAPI
listener.name.sasl_ssl.gssapi.sasl.jaas.config=com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required \
useKeyTab=true \
storeKey=true \
keyTab="/var/lib/secret/kafka.key" \
principal="kafka/kafka.host@REALM";
listener.name.sasl_ssl.scram-sha-512.sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required \
username="admin" \
password="admin-secret";
SASL with KRaft Mode
KRaft mode allows running Kafka without ZooKeeper. While SASL authentication can be used with KRaft, there are some considerations:
-
KRaft-backed clusters cannot use SCRAM for controller-to-controller authentication, though Confluent Server brokers can use SCRAM to authenticate to controllers and other brokers
-
SASL credentials should be created before brokers are running
-
For KRaft with SASL/PLAIN, you need the configuration property
sasl.mechanism.controller.protocol=PLAIN
Best Practices for SASL Authentication
Security Recommendations
-
Always use TLS with SASL to encrypt credentials in transit
-
For production environments, prefer SASL/SCRAM or SASL/GSSAPI over SASL/PLAIN
-
Implement proper credential management and rotation procedures
-
Separate quorum members from brokers in KRaft mode for better fault tolerance
-
Configure ACLs to restrict access to sensitive topics and operations
Mechanism Selection
Choose your SASL mechanism based on your existing infrastructure and security requirements:
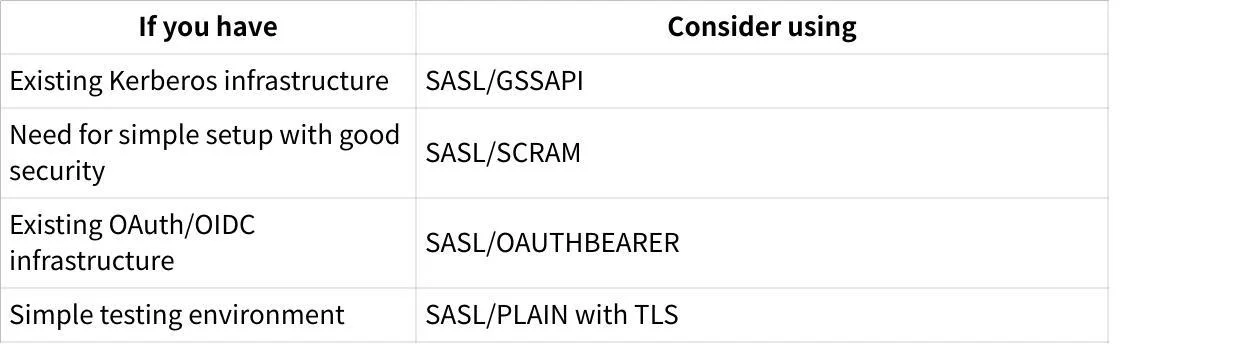
Avoiding Common Issues
-
Always use TLS with SASL/PLAIN to prevent credential exposure
-
Ensure the correct JAAS configuration for each listener and mechanism
-
When using KRaft mode, ensure you've set
super.userscorrectly to allow broker-to-controller communication -
Verify that client configurations match broker configurations for the selected mechanism
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
SaslAuthenticationException
This error indicates authentication failure, typically due to incorrect credentials or misconfiguration. Check:
-
Username and password correctness
-
SASL mechanism configuration
-
JAAS configuration
SSL handshake failed
This occurs when TLS is misconfigured. Ensure:
-
Correct TLS certificates are in place
-
Client and broker truststores/keystores are properly configured
-
The client is connecting to the correct port
Could not find KafkaServer entry in JAAS configuration
In KRaft mode, this indicates JAAS configuration issues. Ensure:
-
Proper JAAS configuration for controllers
-
Setting
sasl.mechanism.controller.protocol=PLAINfor SASL/PLAIN
Unexpected Kafka request of type metadata during sasl handshake
This error suggests the client is not configured for SASL authentication while the server expects it. Verify client configuration matches server expectations.
Conclusion
SASL authentication provides flexible security options for Kafka deployments, from simple username/password authentication to more sophisticated mechanisms like SCRAM and Kerberos. By following the configuration guidelines and best practices outlined in this guide, you can secure your Kafka cluster while meeting your organization's specific security requirements.
Remember that authentication is just one aspect of a comprehensive security strategy for Kafka. Consider combining SASL authentication with TLS encryption, authorization through ACLs, and proper network security measures to create a robust security posture for your Kafka deployment.
If you find this content helpful, you might also be interested in our product AutoMQ. AutoMQ is a cloud-native alternative to Kafka by decoupling durability to S3 and EBS. 10x Cost-Effective. No Cross-AZ Traffic Cost. Autoscale in seconds. Single-digit ms latency. AutoMQ now is source code available on github. Big Companies Worldwide are Using AutoMQ. Check the following case studies to learn more:
-
Grab: Driving Efficiency with AutoMQ in DataStreaming Platform
-
Palmpay Uses AutoMQ to Replace Kafka, Optimizing Costs by 50%+
-
How Asia’s Quora Zhihu uses AutoMQ to reduce Kafka cost and maintenance complexity
-
XPENG Motors Reduces Costs by 50%+ by Replacing Kafka with AutoMQ
-
Asia's GOAT, Poizon uses AutoMQ Kafka to build observability platform for massive data(30 GB/s)
-
AutoMQ Helps CaoCao Mobility Address Kafka Scalability During Holidays
-
JD.com x AutoMQ x CubeFS: A Cost-Effective Journey at Trillion-Scale Kafka Messaging