Google Cloud Pub/Sub has powered event streaming for countless teams. It’s fast, reliable, and fully managed. But as systems grow, many teams hit a wall, with rising costs, limited control, and ecosystem constraints.
You can’t always tune retention. You can’t freely integrate with open-source tools. Every byte of cross-region traffic adds to your bill. The convenience that once felt liberating starts to feel restrictive.
That’s why more data teams are planning a Pub/Sub migration strategy, moving from Pub/Sub to Apache Kafka. Kafka offers open APIs, wide ecosystem support, and complete ownership of your data pipeline. Yet, running Kafka directly in the cloud often introduces new headaches: high replication costs, operational complexity, and scaling friction.
There’s a middle path. A Kafka-compatible platform like AutoMQ delivers the openness of Kafka with the elasticity and efficiency of a cloud-native service. In this article, we’ll explore why organisations are leaving Pub/Sub, what Kafka offers, and how AutoMQ turns migration into a cost-saving, future-proof move.
Why Organisations Consider Migrating from Pub/Sub
Pub/Sub works beautifully at the start. It scales automatically, handles millions of messages, and needs little maintenance. But when traffic grows beyond expectations, its hidden limits begin to surface.
Costs Climb Quickly
Pub/Sub charges for every message, data transfer, and sustained throughput. Cross-region or cross-zone traffic can quietly double cloud bills. For data-intensive platforms, streaming costs often exceed compute costs.
Limited Visibility and Control
Pub/Sub abstracts away infrastructure. That’s convenient, until you need fine-grained tuning. You can’t easily adjust partitioning, retention windows, or consumer behaviour. Latency spikes and delivery retries are difficult to diagnose.
Vendor Lock-in
Pub/Sub is tightly bound to Google Cloud. Integrating with external systems, on-prem clusters, or multi-cloud setups demands connectors and extra services. This dependency limits architectural freedom.
Ecosystem Gaps
Kafka dominates the open-source streaming world. It connects directly to databases, ETL tools, observability stacks, and machine-learning pipelines. Pub/Sub lacks that ecosystem reach.
As data volumes rise and integration demands expand, teams begin to see the trade-off: managed simplicity versus open flexibility. That’s when the Pub/Sub migrate discussion starts, seeking performance, control, and cost predictability beyond Google’s walls.
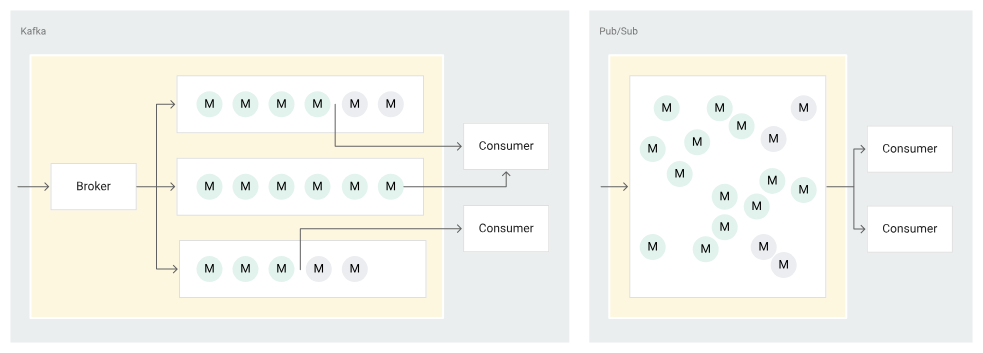
Why Apache Kafka Is a Compelling Choice
Apache Kafka has become the backbone of modern data streaming. It offers what Pub/Sub cannot: openness, flexibility, and control.
Open ecosystem: Kafka isn’t tied to a single cloud provider. It integrates natively with hundreds of open-source and commercial tools, from Spark and Flink to Debezium, Snowflake, and Elasticsearch. This openness lets teams build portable, future-proof data pipelines.
Predictable cost model: Kafka’s storage and throughput are under your control. You can optimise hardware, retention, and replication to match your workload. There’s no opaque billing tied to message count or hidden cross-zone transfers.
Fine-grained control and tuning: Kafka exposes full visibility into partitions, offsets, and consumer groups. Engineers can optimise throughput, replay data, or manage back-pressure precisely, something Pub/Sub keeps out of reach.
Enterprise-grade reliability: Kafka’s design ensures durability and high throughput. It’s trusted at a global scale by companies like LinkedIn, Netflix, and Uber.
But running Kafka in the cloud isn’t without cost. Its “shared-nothing” architecture demands compute, storage, and replication resources that scale together.
Role of a Kafka-Compatible Platform (AutoMQ)
Kafka’s power comes with complexity. Running large Kafka clusters means managing disks, replicas, scaling policies, and cross-zone traffic. In the cloud, this turns into rising operational overhead and unpredictable bills.
That’s where AutoMQ fits in, a new kind of Kafka platform built for the cloud era. It keeps the entire Kafka experience intact but removes the inefficiencies that make Kafka expensive to operate.
100% Kafka API Compatibility
AutoMQ retains Kafka’s compute layer and passes all official Kafka test cases. Every client, connector, and ecosystem tool works exactly as before. Teams can migrate without rewriting a single line of code or losing functionality.
Diskless, Cloud-native Architecture
AutoMQ separates compute from storage. It runs Kafka on shared cloud storage like Amazon S3 or regional EBS. This design cuts replication costs, eliminates local disk bottlenecks, and enables near-instant scaling.
Built-in Efficiency
AutoMQ avoids cross-availability-zone replication, a common hidden cost in cloud Kafka. Benchmarks show up to 10–14× better cost efficiency compared to self-managed Kafka.
Proven in Production
At PalmPay , a leading African fintech platform, AutoMQ replaced Kafka and reduced streaming infrastructure costs by over 50% while processing hundreds of billions of events daily.
AutoMQ delivers Kafka’s openness with cloud-native elasticity and predictable cost. For teams planning a Pub/Sub migrate strategy, it’s the most practical way to gain Kafka’s ecosystem without inheriting its operational burden.
Key Benefits
A Pub/Sub migrate project isn’t just about platform preference; it’s about unlocking new efficiency, flexibility, and visibility. Running Kafka on AutoMQ delivers compounding gains in cost efficiency and scalability.
Major Cost Savings
AutoMQ cuts infrastructure bills dramatically. By removing cross-zone replication and using shared storage, it can deliver up to 10–14× cost efficiency over traditional Kafka setups. Grab achieved 3× lower streaming costs after adopting AutoMQ.
Elastic Scaling in Seconds
Kafka brokers in AutoMQ are stateless. Scaling means adjusting metadata, not shuffling gigabytes of partition data. Clusters expand or contract in seconds — no downtime, no late-night rebalances.
Reuse of the Kafka ecosystem
Because AutoMQ is 100% compatible with the Apache Kafka API, all Kafka connectors, clients, and management tools work instantly. Teams keep their existing pipelines and skills while gaining the benefits of cloud-native operations.
Operational Simplicity
No more manual partition moves or risky rebalancing. AutoMQ’s built-in Self-Balancing component monitors load and redistributes partitions automatically, keeping throughput steady and latency consistent.
Predictable Performance and Latency
With a hybrid of object storage (S3) and low-latency WALs like EBS or FSx, AutoMQ maintains single-digit-millisecond write latency — ideal for microservices, financial systems, and real-time analytics.
Freedom from Vendor Lock-in
Once data pipelines run on Kafka-compatible APIs, workloads can move between clouds freely. The architecture belongs to you, not to any provider.
Migration Roadmap: From Pub/Sub → Kafka (via AutoMQ)
Migrating from Pub/Sub to Kafka isn’t a lift-and-shift exercise. It requires a clear plan to preserve data integrity, minimise downtime, and optimise costs. Here’s a structured roadmap to guide the transition, simplified by AutoMQ’s Kafka compatibility.
Assess Current Pub/Sub Setup
Start with a full inventory. Map topics, message volume, retention settings, and subscriber behaviour. Identify workloads that are latency-sensitive, high-throughput, or cost-heavy; those will benefit most from Kafka’s control and AutoMQ’s efficiency.
Map Concepts to Kafka
Translate Pub/Sub topics and subscriptions into Kafka topics, partitions, and consumer groups. Plan partition counts based on throughput needs, not fixed quotas.
Choose Deployment Path
Decide between self-managed Kafka or a managed, Kafka-compatible platform. AutoMQ lets you deploy inside your own VPC (BYOC model) or as managed software, keeping data private while cutting operational load.
Prepare for Migration
Run a dual-pipeline phase. Forward messages to both Pub/Sub and Kafka simultaneously to validate schema compatibility and consumer readiness. Measure latency, message ordering, and throughput.
Execute the Cut-over
Switch producers and consumers to Kafka endpoints. With AutoMQ’s API compatibility, client changes are minimal. Scale brokers elastically as load stabilises.
Optimise and Monitor
Use Kafka metrics to fine-tune retention, compression, and consumer lag. AutoMQ’s self-balancing feature keeps clusters evenly loaded and responsive.
Considerations & Best Practices
A Pub/Sub migrate strategy brings major benefits, but only if executed with precision. Migration from a managed platform like Pub/Sub to an open system such as Kafka (or AutoMQ) introduces new responsibilities. Here’s what smart teams plan for.
Understand feature differences: Pub/Sub hides complexity. Kafka exposes it. You’ll need to manage partitions, offsets, and retention manually. AutoMQ simplifies much of this, but planning for visibility and alerting is essential.
Map data semantics carefully: Pub/Sub guarantees at-least-once delivery. Kafka provides the same, plus exactly-once in specific configurations. Review consumer logic to ensure identical behaviour during cut-over. Don’t assume equivalence.
Plan for data retention and storage growth: Kafka retains messages for longer by design. Estimate retention periods and choose the right storage class in AutoMQ, object storage for scale, low-latency WAL for speed.
Pilot before full migration: Start with a low-risk stream. Validate compatibility, latency, and cost. Run dual pipelines until metrics are stable and error-free.
Monitor early and often: Kafka provides deep metrics: lag, throughput, partition load. Use them. AutoMQ’s self-balancing and integrated monitoring make it easier, but human oversight remains key during the first weeks.
Train your team: Kafka introduces new operational skills. Empower DevOps and data engineers with basic Kafka commands, offset management, and cluster health checks.
A careful start ensures a stable finish. The goal isn’t just migration, it’s mastery of a streaming stack that you fully control and truly understand.
Conclusion
Migrating from Pub/Sub to Kafka is a step toward control and scalability. Pub/Sub offers simplicity, but its costs and limits grow with your data. AutoMQ keeps Kafka’s openness while making it cloud-native, diskless, elastic, and cost-efficient. It’s the same Kafka experience, faster and lighter. For teams planning a Pub/Sub migration journey, AutoMQ turns migration into an upgrade, simpler operations, lower cost, and complete freedom to scale.
Interested in our diskless Kafka solution, AutoMQ? See how leading companies leverage AutoMQ in their production environments by reading our case studies. The source code is also available on GitHub.
Grab: Driving Efficiency with AutoMQ in DataStreaming Platform
Palmpay Uses AutoMQ to Replace Kafka, Optimizing Costs by 50%+
How Asia’s Quora Zhihu uses AutoMQ to reduce Kafka cost and maintenance complexity
XPENG Motors Reduces Costs by 50%+ by Replacing Kafka with AutoMQ
Asia's GOAT, Poizon uses AutoMQ Kafka to build observability platform for massive data(30 GB/s)
AutoMQ Helps CaoCao Mobility Address Kafka Scalability During Holidays
JD.comx AutoMQ x CubeFS: A Cost-Effective Journey at Trillion-Scale Kafka Messaging














.png)