In today’s cloud-driven world, data streaming infrastructure is being reshaped by the need for elasticity, cost efficiency, and simplified operations. Apache Kafka, originally designed for static, disk-based environments, faces challenges in hyperscale cloud deployments where local broker disks become bottlenecks, limiting scalability and increasing replication and cross-zone traffic costs.
Diskless Kafka represents a fundamental evolution in this architecture. By separating compute from storage and moving data persistence directly to shared cloud object storage — such as Amazon S3, AWS S3 Express, or Google Cloud Storage — it eliminates the dependency on local disks and the need for replication-heavy scaling.
AutoMQ leads this transformation. Built directly on the Apache Kafka codebase, AutoMQ is the world’s first production-grade Diskless Kafka, combining cloud-native elasticity, low-latency streaming, and full Kafka protocol compatibility. It enables enterprises to achieve faster, more cost-efficient, and simpler real-time data streaming, while maintaining full compatibility with the existing Kafka ecosystem.
Key Takeaways
Diskless Kafka removes local disks and stores data directly in shared cloud storage such as Amazon S3, enabling fully elastic and cloud-native streaming.
AutoMQ is the world’s first production-ready Diskless Kafka, built on the Apache Kafka codebase with 100% Kafka API compatibility.
Table Topic, AutoMQ’s advanced integration feature, synchronizes Kafka streams directly with Apache Iceberg tables, unifying streaming and batch data into a single, governed data architecture.
The future of Kafka is diskless — and AutoMQ makes it faster, simpler, and truly optimized for the cloud era.
What Does “Diskless Kafka” Mean?
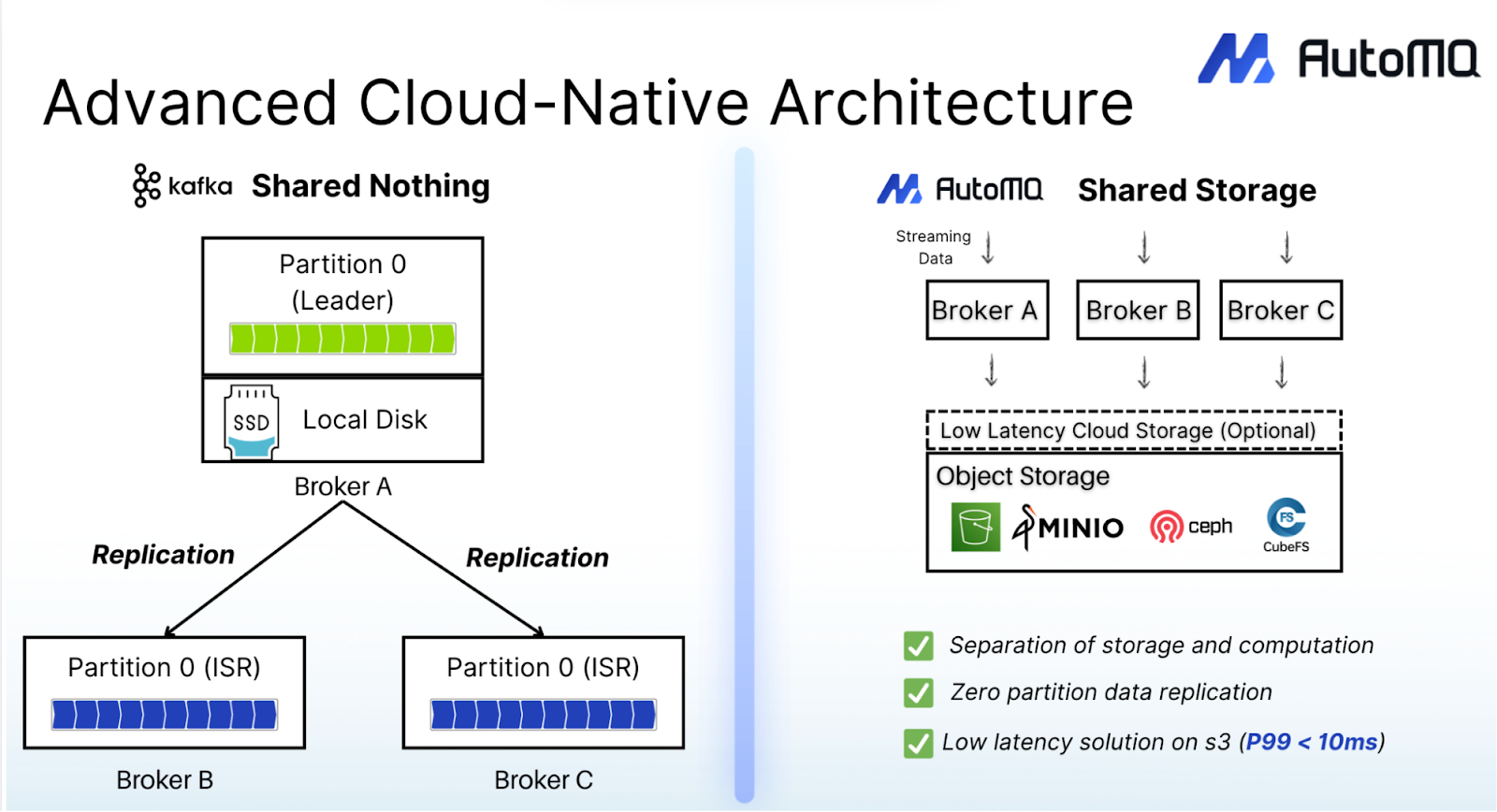
Diskless Kafka redefines the foundation of Kafka’s architecture by separating compute from storage. Instead of persisting logs on local broker disks, messages are written directly to shared cloud storage such as Amazon S3, AWS S3 Express, or Google Cloud Storage (GCS).
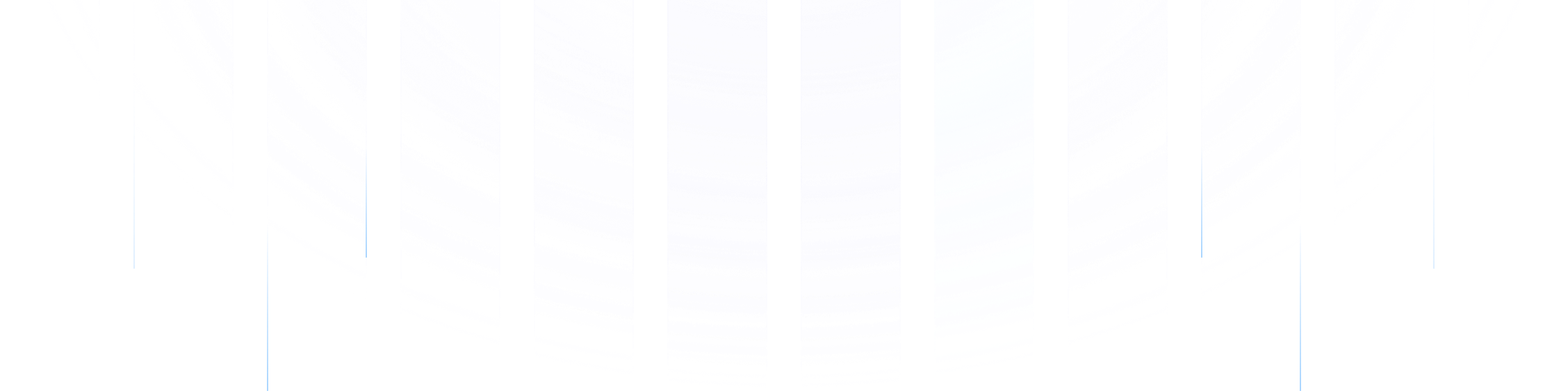
In this architecture, Kafka brokers act as stateless compute nodes, responsible for processing messages rather than storing them. Partition information is maintained through lightweight metadata communication between brokers, while message data is durably stored in shared cloud storage.
Because cloud storage services inherently provide redundancy and durability, Kafka’s traditional in-sync replica (ISR) mechanism for fault tolerance becomes unnecessary. The result is a cloud-native, diskless design that scales elastically, recovers rapidly, and operates at lower cost — without the operational overhead of managing local disks or replica synchronization.
How Diskless Kafka Works
Diskless Kafka modernizes data streaming by fully decoupling compute and storage, aligning with the architectural principles of the cloud. Instead of writing log segments to local disks, data is written directly to shared cloud storage — the same approach used in AutoMQ’s production-ready implementation.
When a producer sends messages, the broker first writes them to a small, fixed-capacity, low-latency storage that serves as a Write-Ahead Log (WAL). This ensures fast acknowledgment and stable throughput. The data is then asynchronously uploaded to shared cloud storage such as Amazon S3, Regional EBS, or FSx, where it is durably persisted.
This diskless, shared-storage architecture brings several key operational advantages:
Stateless Brokers: Brokers can be added or removed without data migration or rebalancing storms.
No Replication Overhead: Shared cloud storage ensures durability, eliminating the need for ISR replication and cross-AZ network traffic.
Independent Scaling: Compute and storage scale independently, allowing dynamic elasticity and optimized resource utilization.
Simplified Recovery: Partition reassignment and scaling occur through lightweight metadata communication rather than large-scale data transfers.
The Limitations of Traditional Kafka Architecture
Apache Kafka has long powered mission-critical data streaming pipelines across global enterprises. However, its original shared-nothing architecture, designed for on-premises environments, exposes major challenges when deployed in the cloud.
Each Kafka broker stores log data on local disks, tightly coupling compute and storage. As workloads grow or traffic patterns shift, rebalancing partitions across brokers requires large-scale data replication, which creates latency spikes, operational complexity, and significant cross-zone network traffic. In multi-AZ or multi-region deployments, replication overhead can account for a substantial portion of total cloud spend — in some cases exceeding 80% of infrastructure cost, according to Confluent’s published analysis.
Kafka’s In-Sync Replica (ISR) mechanism further increases CPU and network utilization in dynamic cloud clusters. Scaling or replacing brokers requires lengthy data migrations, while uneven disk utilization often forces operators to over-provision computing resources to maintain stability.
These architectural constraints make it difficult for traditional Kafka to take advantage of cloud-native shared storage and elastic scaling. In short, Kafka’s original design was optimized for physical servers — not the on-demand, flexible infrastructure of the cloud era.
AutoMQ: The World’s First Production-Ready Diskless Kafka
AutoMQ is the only production-ready, open-source Diskless Kafka for Cloud, delivering enterprise-grade performance, 100 % Kafka API compatibility, and operational simplicity — all while running natively on shared cloud storage.
Built directly on the Apache Kafka codebase, AutoMQ fully retains Kafka’s compute layer and re-implements only its storage layer. Local disk persistence is replaced with a shared-storage architecture powered by services such as Amazon S3, Regional EBS, or FSx, enabling AutoMQ to maintain complete compatibility across the Kafka ecosystem — including Strimzi Operator, Schema Registry, and Kafka Connect — with no changes required at the application level.
Compatibility and reliability are proven, not theoretical:
1,000 + KIPs implemented
387 Apache Kafka test cases passed
Code gap < 2 months with the latest Apache Kafka release
AutoMQ’s shared-storage design eliminates replication overhead and cross-AZ network traffic. It delivers the elasticity, low latency, and operational simplicity required by cloud-native environments — all without disrupting the Kafka ecosystem enterprises already depend on.
How Diskless Kafka Works with AutoMQ
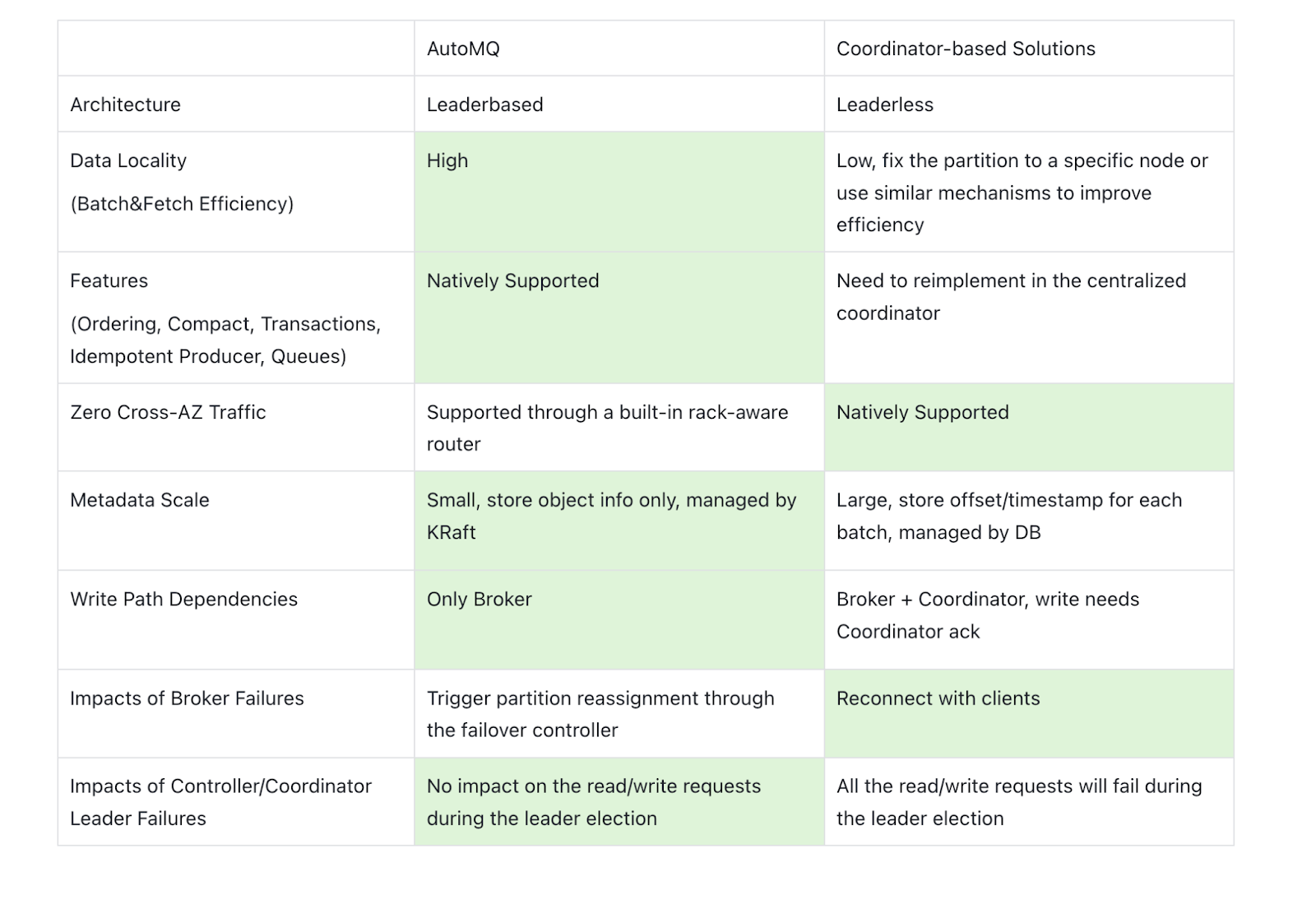
AutoMQ brings the Diskless Kafka concept from theoretical proposal to production-grade reality by combining Kafka’s proven leader-based coordination model with a cloud-native shared-storage architecture.
Hybrid Data Path for Low Latency
AutoMQ accelerates producer writes by using a small, fixed-capacity, low-latency storage as a Write-Ahead Log (WAL). Data is first written to this WAL for rapid acknowledgment and then asynchronously uploaded to shared cloud storage such as Amazon S3, Regional EBS, or FSx. This hybrid design achieves sub-10 ms latency while maintaining full durability through cloud storage.
Leader-Based Coordination
Unlike KIP-1150’s leaderless architecture, AutoMQ preserves Kafka’s leader-based model, ensuring message ordering, transactional guarantees, and exactly-once semantics. This design maintains complete compatibility with Kafka’s protocol and operational stability.
Instant Scaling and Compatibility
AutoMQ’s diskless architecture makes brokers stateless. When scaling out, only lightweight metadata communication between brokers is needed to complete partition reassignment — without moving local disk data or performing partition rebalancing. AutoMQ reuses 98 % of the Apache Kafka codebase, passes all Kafka test suites, and has already been adopted by enterprises such as Grab, Zhihu, and Geely Auto.
Together, these capabilities allow AutoMQ to deliver a cloud-native, production-ready Diskless Kafka that combines low latency, seamless elasticity, and full Kafka compatibility.
Benefits of Diskless Kafka with AutoMQ
Diskless Kafka fundamentally reshapes both the operational efficiency and cost structure of running Kafka in the cloud. AutoMQ’s shared-storage architecture brings measurable advantages across elasticity, performance, and reliability.
Effortless Elasticity
Because all partition data is stored in shared cloud storage, brokers can be scaled up or down within seconds. There is no need for data replication or rebalancing, and scaling requires only lightweight metadata communication. AutoMQ supports multi-cluster and Kubernetes-based hybrid deployments, providing true cloud-native elasticity.
Cloud Cost Optimization
Traditional Kafka clusters require fixed resource reservations for compute and disks, often leading to underutilization. AutoMQ’s diskless architecture eliminates local disk dependencies and leverages pay-as-you-go cloud storage such as Amazon S3 and GCS. Benchmarked deployments, including those by Grab , have achieved up to 3× cost efficiency while maintaining full durability.
Low Latency, High Throughput
AutoMQ uses low-latency storage as a Write-Ahead Log (WAL) and asynchronously uploads data to shared storage. This hybrid design enables single-digit millisecond write latency and significantly improves throughput per CPU core compared to traditional Kafka.
Simplified Operations & Reliability
AutoMQ’s stateless brokers eliminate inter-broker replication, minimizing failure impact and operational overhead. The shared-storage architecture provides automatic durability and high availability , ensuring reliability without manual intervention.
100% Kafka Compatibility
AutoMQ is built directly on the Apache Kafka codebase, retaining 100% API compatibility . It passes all Kafka test suites, allowing developers to use existing producers, consumers, and Kafka connectors without modification.
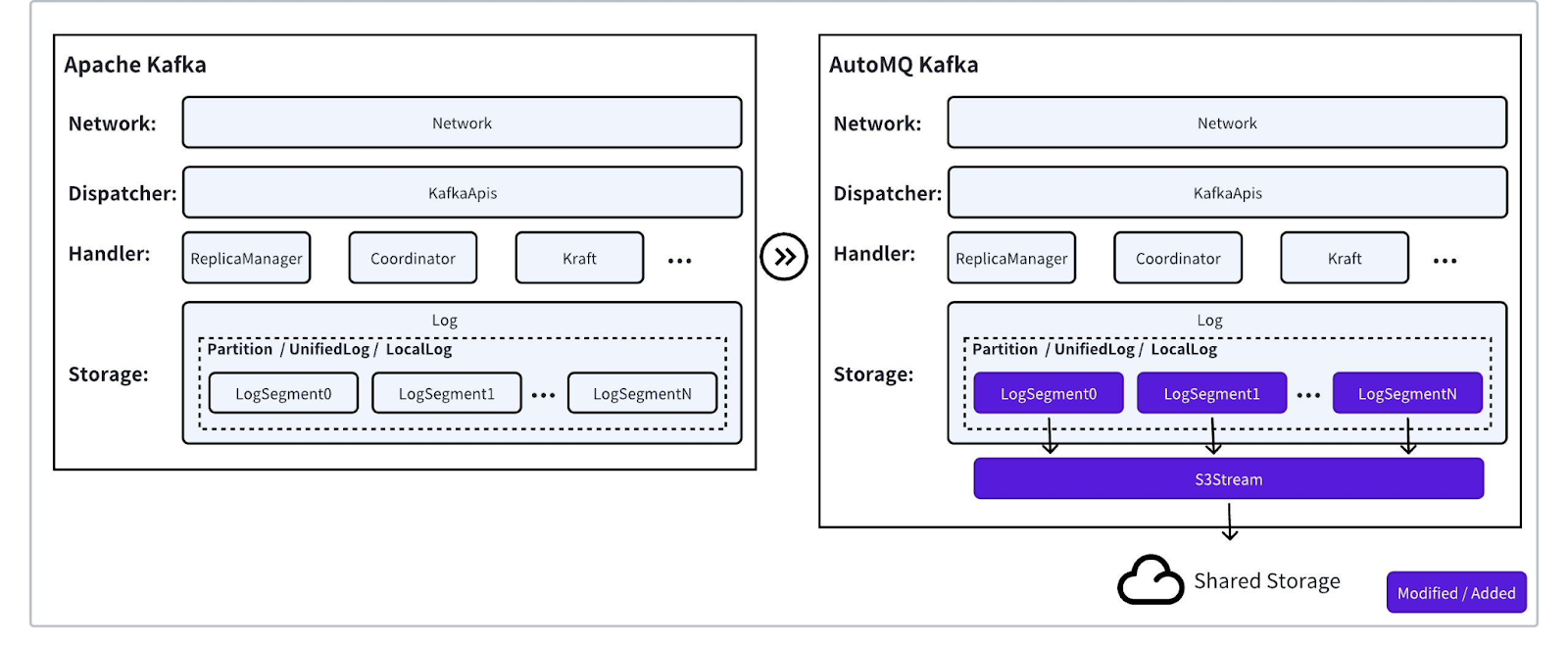
Future-Proof Integration
AutoMQ extends Diskless Kafka through its Table Topic feature, enabling direct synchronization between Kafka streams and Apache Iceberg tables . This unifies real-time and batch data into a single, analytics-ready architecture.
Diskless Kafka vs. KIP-1150
Diskless Kafka represents a major architectural evolution in the Kafka ecosystem. However, achieving a production-ready, cloud-native implementation requires deep engineering maturity.
KIP-1150 introduced the concept of diskless topics for Apache Kafka, proposing a leaderless coordination model managed by a new Batch Coordinator component. While this proposal explored the potential of separating compute and storage, it sacrificed exactly-once semantics and broke compatibility with the existing Kafka protocol. Subsequent proposals — KIP-1163, KIP-1164, and KIP-1183 — continue to refine these ideas, but all remain experimental and have not yet been merged into Apache Kafka’s mainline release.
AutoMQ, in contrast, implements a leader-based coordination model that fully retains Kafka’s reliability, ordering, and transactional guarantees. Built directly on the Kafka codebase, AutoMQ eliminates replication overhead through its shared-storage architecture while maintaining 100 % Kafka API compatibility.
AutoMQ is currently the only production-ready implementation of Diskless Kafka, already adopted by enterprises such as Grab and Geely Auto. With proven stability, protocol consistency, and cloud-native scalability, AutoMQ represents the most mature and deployable realization of diskless topics available today.
The Future of Kafka Is Diskless
The next generation of Kafka is defined by the separation of compute and storage. AutoMQ fully embodies this evolution, replacing replication-heavy, disk-based architecture with a shared cloud storage foundation that is faster, simpler, and built for elasticity at cloud scale.
By eliminating replication complexity and leveraging stateless brokers, AutoMQ reduces infrastructure cost and operational overhead while enabling real-time scalability.
As the only open-source, production-ready Diskless Kafka that maintains 100 % Kafka API compatibility, AutoMQ demonstrates that the future of Kafka is not about adding more disks or replicas — it’s about removing them.
With AutoMQ, the diskless, cloud-native future of Kafka has already arrived.
Beyond Diskless: AutoMQ Table Topic and the Future of Unified Streaming
The move to Diskless Kafka does more than modernize architecture — it expands Kafka’s capabilities into unified data management. By separating compute from storage, AutoMQ enables real-time streaming data to integrate seamlessly with analytical and batch processing systems. The most powerful example of this evolution is AutoMQ’s Table Topic, which bridges Kafka topics and Apache Iceberg tables in one step.
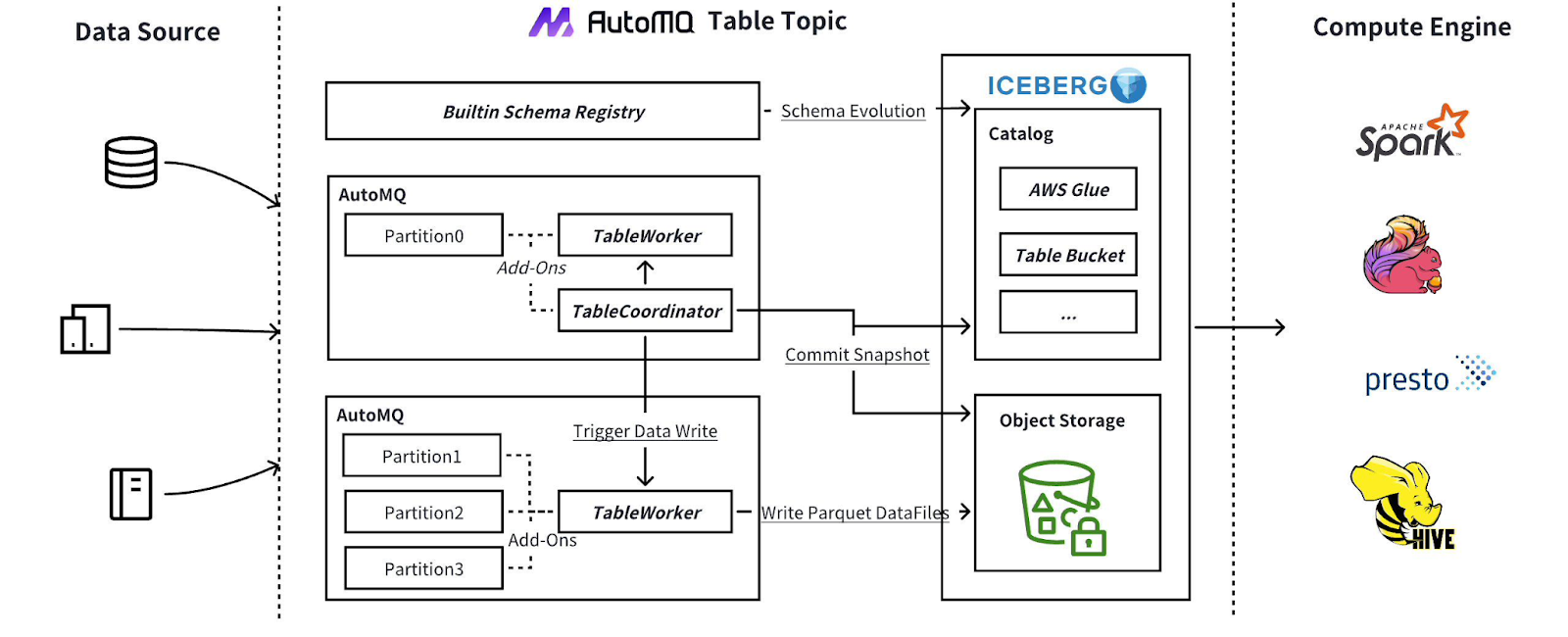
From Streams to Tables
Table Topic enables a one-step conversion from Kafka Topic to Iceberg Table, transforming continuous event streams into structured, queryable datasets. This unifies real-time and historical data, enabling low-latency analytics, consistent schema evolution, and centralized governance within the same data environment.
Enabled by Diskless Design
Because AutoMQ’s Diskless Kafka already uses shared cloud storage, Table Topic can expose streaming data directly as Iceberg-compatible tables without additional ETL or data movement. This architecture creates a unified, analytics-ready data layer, bridging the gap between streaming and batch systems.
Unified Data Lifecycle
AutoMQ’s Table Topic allows organizations to:
Perform real-time analytics on live streaming data.
Conduct historical analysis using the same data stored in Iceberg tables.
Maintain consistent governance and schema management across both streaming and batch pipelines.
Built upon the Diskless Kafka foundation, AutoMQ transforms Kafka from a pure streaming platform into a unified data engine, connecting operational workloads with the analytical power of the modern data lakehouse.
Conclusion
The era of Diskless Kafka has arrived. Built directly on the Apache Kafka codebase, AutoMQ redefines what streaming data infrastructure can achieve in the cloud. By introducing a shared cloud storage architecture, AutoMQ delivers a Kafka that is faster, more cost-efficient, simpler to operate, and natively elastic.
As the only open-source, production-ready Diskless Kafka, AutoMQ maintains 100 % Kafka API compatibility while eliminating replication overhead and cross-AZ network cost. It provides the scalability, performance, and reliability that modern cloud environments demand.
From zero-replication cost to Table Topic integration, AutoMQ transforms Kafka from a disk-bound system into a fully cloud-native, analytics-ready platform — proving that the future of Kafka is not only diskless, but also unified, intelligent, and built for the cloud-first world.
Interested in our diskless Kafka solution AutoMQ? See how leading companies leverage AutoMQ in their production environments by reading our case studies. The source code is also available on GitHub.
Grab: Driving Efficiency with AutoMQ in DataStreaming Platform
Palmpay Uses AutoMQ to Replace Kafka, Optimizing Costs by 50%+
How Asia’s Quora Zhihu uses AutoMQ to reduce Kafka cost and maintenance complexity
XPENG Motors Reduces Costs by 50%+ by Replacing Kafka with AutoMQ
Asia's GOAT, Poizon uses AutoMQ Kafka to build observability platform for massive data(30 GB/s)
AutoMQ Helps CaoCao Mobility Address Kafka Scalability During Holidays
JD.comx AutoMQ x CubeFS: A Cost-Effective Journey at Trillion-Scale Kafka Messaging














.png)